Di-aqua-bis-(cinnamato-κ(2) O,O')cadmium
- PMID: 24764939
- PMCID: PMC3998447
- DOI: 10.1107/S160053681400364X
Di-aqua-bis-(cinnamato-κ(2) O,O')cadmium
Abstract
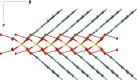
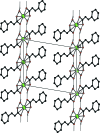
The title complex, [Cd(C9H7O2)2(H2O)2], was obtained as an unintended product of the reaction of cadmium nitrate with hexa-methyl-ene-tetra-mine and cinnamic acid. The Cd(II) ion lies on a twofold rotation axis and is coordinated in a slightly distorted trigonal-prismatic environment. In the crystal, the V-shaped mol-ecules are arranged in an inter-locking fashion along [010] and O-H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the mol-ecules, forming a two-dimensional network parallel to (001).
Figures



References
-
- Allen, F. H. (2002). Acta Cryst. B58, 380–388. - PubMed
-
- Amma, E. L., Griffith, E. A. H., Charles, N. G. & Rodesiler, P. F. (1983). ACS Abstr. Papers, p. 39.
-
- Bruker (2012). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Hosomi, H., Ohba, S. & Ito, Y. (2000). Acta Cryst. C56, e123. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
