Autophagy: A novel therapeutic target for hepatocarcinoma (Review)
- PMID: 24765136
- PMCID: PMC3997714
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2014.1916
Autophagy: A novel therapeutic target for hepatocarcinoma (Review)
Abstract
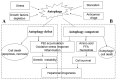
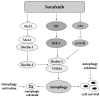
Autophagy is a highly conserved intracellular degradation process and plays an important role in hepatocarcinogenesis. Available data show that autophagy is involved in anti-hepatocarcinoma (HCC) therapies. Autophagy regulation involves a novel target for overcoming therapeutic resistance and sensitizing HCC to currently therapeutic methods. This is a systematic review on the interface of autophagy and the development of HCC and outlining the role of autophagy in current anti-HCC approaches. Understanding the significance of autophagy in anti-HCC therapy may offer a novel therapeutic target for improving anti-cancer efficacy and prolong survival for HCC patients.
Keywords: anti-hepatocarcinoma therapy; autophagy; hepatocarcinoma.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
