Effects of epidermal growth factor on the invasive activity and cytoskeleton of oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines
- PMID: 24765152
- PMCID: PMC3997698
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2014.1946
Effects of epidermal growth factor on the invasive activity and cytoskeleton of oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines
Abstract
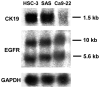
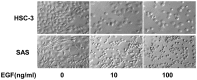
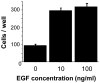
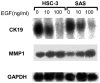
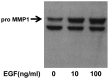
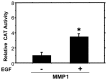
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is present at high concentrations in human saliva and modulates the growth and differentiation of various cancer cells. To elucidate the molecular mechanisms by which EGF affects oral cancer proliferation and invasion, the current study analyzed the Matrigel invasion activity of cultured oral cancer cell lines. Cell proliferation under the influence of EGF was subjected to Matrigel invasion assays, and cell proliferation in the absence of EGF was used as control. Northern blot analyses quantified the invasiveness and tumorigenicity. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase assay determined the EGF stimulation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 1 expression. EGF increased the number of cells penetrating the Matrigel membrane. Northern blot analysis revealed that MMP1 and cytokeratin 19 expression correlate with EGF. In addition, the morphology of HSC-3 and SAS cells changed following the addition of EGF to the culture medium. A transient transfection assay revealed that EGF increases the promoter activities of MMP1 in HSC-3 cells. These observations suggested that EGF increases the invasive activity of oral cancer cells, partly by increasing MMP1, and morphological changes may be induced by altering the composition of cytoskeletal proteins.
Keywords: cytokeratin 19; epidermal growth factor; matrix metalloproteinase 1; matrix metalloproteinases; squamous cell carcinoma.
Figures
References
-
- Cohen S. Isolation of a mouse submaxillary gland protein accelerating incisor eruption and eyelid opening in the new-born animal. J Biol Chem. 1962;237:1555–1562. - PubMed
-
- Kawamata H, Azuma M, Kameyama S, Nan L, Oyasu R. Effect of epidermal growth factor/transforming growth factor alpha and transforming growth factor beta 1 on growth in vitro of rat urinary bladder carcinoma cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1992;3:819–825. - PubMed
-
- Kuranami M, Tamaguchi K, Fuchigami M, et al. Effect of urine on clonal growth of human bladder cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 1991;51:4631–4635. - PubMed
-
- Ishikawa J, Maeda S, Sugiyama T, et al. EGF stimulates anchorage-independent growth of a human bladder carcinoma cell line (KU1) with an amplified and over-expressed EGF receptor gene. Int J Cancer. 1989;44:1000–1004. - PubMed
-
- Chen LL, Narayanan R, Hibbs MS, et al. Altered epidermal growth factor signal transduction in activated Ha-ras transformed human keratinocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993;193:167–174. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
