Fermentation supernatants of Lactobacillus delbrueckii inhibit growth of human colon cancer cells and induce apoptosis through a caspase 3-dependent pathway
- PMID: 24765211
- PMCID: PMC3997687
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2014.1959
Fermentation supernatants of Lactobacillus delbrueckii inhibit growth of human colon cancer cells and induce apoptosis through a caspase 3-dependent pathway
Abstract
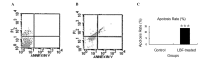
Probiotic bacteria are known to exert a wide range of beneficial effects on their animal hosts. Therefore, the present study explored the effect of the supernatants obtained from Lactobacillus delbrueckii fermentation (LBF) on colon cancer. The results indicated that the proliferation of LBF solution-treated colon cancer SW620 cells was arrested and accumulated in the G1 phase in a concentration-dependent manner. The LBF solution efficiently induced apoptosis through the intrinsic caspase 3-depedent pathway, with a corresponding decreased expression of Bcl-2. The activity of matrix metalloproteinase 9, which is associated with the invasion of colon cancer cells, was also decreased in the LBF-treated cells. In conclusion, the results demonstrate the antitumor effect of LBF in vitro and may contribute to the development of novel therapies for the treatment of colon cancer.
Keywords: Lactobacillus delbrueckii; apoptosis; caspase 3; colon cancer; matrix metalloproteinase-9.
Figures



References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Watson AJ, Collins PD. Colon cancer: a civilization disorder. Dig Dis. 2011;29:222–228. - PubMed
-
- Tjalsma H, Boleij A, Marchesi JR, et al. A bacterial driver-passenger model for colorectal cancer: beyond the usual suspects. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012;10:575–582. - PubMed
-
- Rafter J. Probiotics and colon cancer. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2003;17:849–859. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
