Mucormycosis of the hard palate masquerading as carcinoma
- PMID: 24765427
- PMCID: PMC3981330
- DOI: 10.4081/cp.2012.e28
Mucormycosis of the hard palate masquerading as carcinoma
Abstract
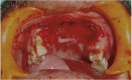
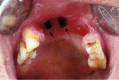
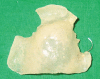
A growing number of medically compromised patients are encountered by dentists in their practices. Opportunistic fungal infections such as mucormycosis usually occur in immunocompromised patients but can infect healthy individuals as well. Mucormycosis is an acute opportunistic, uncommon, frequently fatal fungal infection, caused by a saprophytic fungus that belongs to the class of phycomycetes. Among the clinical differential diagnosis we can consider squamous cell carcinoma. Such cases present as chronic ulcers with raised margins causing exposure of underlying bone. There is a close histopathological resemblance between mucormycosis and aspergillosis. Microscopically, aspergillosis has septate branching hyphae, which can be distinguished from mucormycotic hyphae by a smaller width and prominent acute angulations of branching hyphae. A definitive diagnosis of mucormycosis can be made by tissue biopsy that identifies the characteristic hyphae, by positive culture or both. The culture of diseased tissue may be negative and histopathologic examination is essential for early diagnosis. Mucormycosis was long regarded as a fatal infection with poor prognosis. However with early medical and surgical management survival rates are now thought to exceed 80%. In the present case, the fungus was identified by hematoxylin and eosin stain and confirmed by Grocott's silver methenamine special staining technique. Removal of the necrotic bone, which acted as a nidus of infection, was done. Post-operatively patient was advised an obturator to prevent oronasal regurgitation. Since mucormycosis occurs infrequently, it may pose a diagnostic and therapeutic dilemma for those who are not familiar with its clinical presentation.
Keywords: fungal infection; mucormycosis; necrotic bone; phycomycetes; squamous cell carcinoma..
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: the authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Ruoppi P, Dietz A, Nikanne E, et al. Paranasal sinus mucormycosis: a report of two cases. Acta Otolaryngol. 2001;121:948–52. - PubMed
-
- Ketenci I, Unlü Y, Sentürk M, Tuncer E. Indolent mucormycosis of the sphenoid sinus. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2005;132:341–2. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharyya AK, Deshpande AR, Nayak SR, et al. Rhinocerebral mucormycosis: an unusual case presentation. J Laryngol Otol. 1992;106:48–9. - PubMed
-
- Marx RE, Stern D. 1st ed. Hanover Park, IL: Quintessence Publishing Co, Inc; 2006. Oral and maxillofacial pathology: a rationale for diagnosis and treatment; pp. 104–106.
-
- Salisbury PL, 3rd, Caloss R, Jr, Cruz JM, et al. Mucormycosis of the mandible after dental extractions in a patient with acute myelogenus leukemia. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1997;83:340–4. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

