Use of therapeutic surfactant lavage in a preterm infant with massive pulmonary hemorrhage
- PMID: 24765473
- PMCID: PMC3981312
- DOI: 10.4081/cp.2012.e74
Use of therapeutic surfactant lavage in a preterm infant with massive pulmonary hemorrhage
Abstract
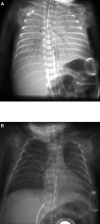
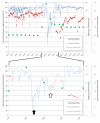
We report a case of a premature infant presenting with recurrent pulmonary hemorrhage in which we performed a therapeutic lavage with diluted surfactant after an acute episode of bleeding with severe intractable hypoxemia. Repeated small aliquots of diluted surfactant (10×2 mL) allowed rapid improvement in oxygenation and reduction of required mean airway pressures during high frequency oscillatory ventilation. This observation may suggest that surfactant lavage could be beneficial in massive pulmonary hemorrhage in infants. A randomized controlled trial might be needed to clarify the potential benefit of this therapeutic intervention on outcome of infants suffering from this life-threatening complication.
Keywords: prematurity.; pulmonary hemorrhage; surfactant lavage.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests: the authors declare no potential conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Berger TM, Allred EN, Van Marter LJ. Antecedents of clinically significant pulmonary hemorrhage among newborn infants. J Perinatol. 2000;20:295–300. - PubMed
-
- Finer NN. Surfactant use for neonatal lung injury: beyond respiratory distress syndrome. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2004;5(Suppl A):S289–97. - PubMed
-
- Sweet DG, Halliday HL. The use of surfactants in 2009. Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed. 2009;94:78–83. - PubMed
-
- Dargaville PA, Mills JF. Surfactant therapy for meconium aspiration syndrome: current status. Drugs. 2005;65:2569–91. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

