Current advancements and potential strategies in the development of MERS-CoV vaccines
- PMID: 24766432
- PMCID: PMC4241375
- DOI: 10.1586/14760584.2014.912134
Current advancements and potential strategies in the development of MERS-CoV vaccines
Abstract
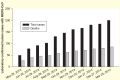
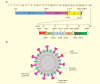
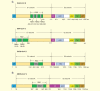
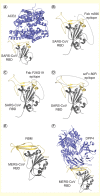
Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) is a newly emerging infectious disease caused by a novel coronavirus, MERS-coronavirus (MERS-CoV), a new member in the lineage C of β-coronavirus (β-CoV). The increased human cases and high mortality rate of MERS-CoV infection make it essential to develop safe and effective vaccines. In this review, the current advancements and potential strategies in the development of MERS vaccines, particularly subunit vaccines based on MERS-CoV spike (S) protein and its receptor-binding domain (RBD), are discussed. How to improve the efficacy of subunit vaccines through novel adjuvant formulations and routes of administration as well as currently available animal models for evaluating the in vivo efficacy of MERS-CoV vaccines are also addressed. Overall, these strategies may have important implications for the development of effective and safe vaccines for MERS-CoV in the future.
Keywords: MERS-CoV; Middle East respiratory syndrome; adjuvants; administration routes; coronavirus; receptor-binding domain; spike protein; subunit vaccines; vaccines.
Figures
References
-
- Zaki AM, van Boheemen S, Bestebroer TM, et al.. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N Engl J Med 2012;367(19):1814-20 - PubMed
-
First report about the isolation of Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) coronavirus (MERS-CoV) in humans.
-
- WHO Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. (MERS-CoV) - update. Available from: www.who.int/csr/don/2014_03_26/en/ [Last accessed 26 March 2014] - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
