Insufficient interleukin-12 signalling favours differentiation of human CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells into GATA-3(+) and GATA-3(+) T-bet(+) subsets in humanized mice
- PMID: 24766459
- PMCID: PMC4172137
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.12304
Insufficient interleukin-12 signalling favours differentiation of human CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells into GATA-3(+) and GATA-3(+) T-bet(+) subsets in humanized mice
Abstract
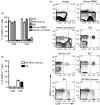
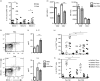
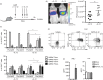
Differentiation of CD4(+) T cells into type 1 or type 2 subsets is mediated by the expression of the opposing lineage defining transcription factors T-bet and GATA-3. However, the existence of GATA-3(+) T-bet(+) CD4(+) T cells in mice suggests functional plasticity of these subsets. Little is known about type 1 and type 2 plasticity of human T-cell subsets in vivo. Here, we show that in the xenogeneic environment of humanized mice, which lacks a functional immune-regulatory network, human CD4(+) and, notably, CD8(+) T cells preferentially differentiate into interleukin (IL)-4(+) GATA-3(+) and IL-4(+) interferon-γ(+) GATA-3(+) T-bet(+) subsets. Treatment with recombinant human IL-12 or expansion of IL-12-producing human dendritic cells in vivo reverted this phenotype and led to the down-regulation of GATA-3 expression. These changes also correlated with improved antiviral immune responses in humanized mice. In conclusion, our study shows the capacity of human CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells for stable co-expression of GATA-3 and T-bet in humanized mice and reveals a critical role for IL-12 in regulating this phenotype.
Keywords: T-cell plasticity; humanized mice; interleukin-12.
© 2014 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures






References
-
- Mosmann TR, Coffman RL. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–73. - PubMed
-
- Szabo SJ, Kim ST, Costa GL, Zhang X, Fathman CG, Glimcher LH. A novel transcription factor, T-bet, directs Th1 lineage commitment. Cell. 2000;100:655–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

