Population pharmacokinetic meta-analysis of vortioxetine in healthy individuals
- PMID: 24766668
- PMCID: PMC4257570
- DOI: 10.1111/bcpt.12256
Population pharmacokinetic meta-analysis of vortioxetine in healthy individuals
Abstract
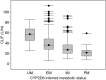
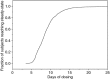
The objective was to describe the pharmacokinetics of vortioxetine and evaluate the effect of intrinsic and extrinsic factors in the healthy population. Data from 26 clinical pharmacology studies were pooled. A total of 21,758 vortioxetine quantifiable plasma concentrations were collected from 887 subjects with corresponding demography. The doses ranged from 2.5 to 75 mg (single dose) and 2.5-60 mg (multiple QD doses). The pharmacokinetics of vortioxetine was best characterised by a two-compartment model with first-order absorption, lag-time and linear elimination, with interindividual error terms for absorption rate constant, oral clearance and central volume of distribution. The population mean was 32.7 L/hr for oral clearance and 1.97∙10(3) L for the central volume of distribution. The average elimination half-life was 65.8 hr. CYP2D6 inferred metabolic status (ultra, extensive, intermediate or poor metabolisers) and age on oral clearance and height on central volume of distribution were identified as statistically significant covariate-parameter relationships. For CYP2D6 poor metabolisers, CL/F was approximately 50% to that seen in CYP2D6 extensive metabolisers. The impact of height on V2/F and age on CL/F was low and not considered to be clinically relevant. The final model was found to be reliable, stable and predictive. A reliable, stable and predictive pharmacokinetic model was developed to characterise pharmacokinetics of vortioxetine in the healthy population.
© 2014 The Authors. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Nordic Association for the Publication of BCPT (former Nordic Pharmacological Society).
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization. Mental health: depression. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs369/en/. (last accessed on 21 January 2014)
-
- Bang-Andersen B, Ruhland T, Jørgensen M, Smith G, Frederiksen K, Jensen KG, et al. Discovery of 1-[2-(2,4-dimethylphenylsulfanyl)phenyl]piperazine (Lu AA21004): a novel compound for the treatment of mood and anxiety disorders. J Med Chem. 2011;54:3206–21. - PubMed
-
- Millan MJ. Multi-target strategies for the improved treatment of depressive states: conceptual foundations and neuronal substrates, drug discovery and therapeutic application. Pharmacol Ther. 2006;110:135–370. - PubMed
-
- Areberg J, Søgaard B, Højer A-M. The clinical pharmacokinetics of Lu AA21004 and its major metabolite in healthy young volunteers. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2012;111:198–205. - PubMed
-
- Hvenegaard MG, Bang-Andersen B, Pedersen H, Jørgensen M, Püschl A, Dalgaard L. Identification of the cytochrome P450 and other enzymes involved in the in vitro oxidative metabolism of a novel antidepressant, Lu AA21004. Drug Metab Dispos. 2012;40:1357–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

