Serum C-X-C motif chemokine 13 is elevated in early and established rheumatoid arthritis and correlates with rheumatoid factor levels
- PMID: 24766912
- PMCID: PMC4060390
- DOI: 10.1186/ar4552
Serum C-X-C motif chemokine 13 is elevated in early and established rheumatoid arthritis and correlates with rheumatoid factor levels
Abstract
Introduction: We hypothesized that serum levels of C-X-C motif chemokine 13 (CXCL13), a B-cell chemokine, would delineate a subset of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients characterized by increased humoral immunity.
Methods: Serum from patients with established RA (the Dartmouth RA Cohort) was analyzed for CXCL13, rheumatoid factor (RF) levels, anticitrullinated peptide/protein antibody (ACPA) and total immunoglobulin G (IgG); other parameters were obtained by chart review. A confirmatory analysis was performed using samples from the Sherbrooke Early Undifferentiated PolyArthritis (EUPA) Cohort. The Wilcoxon rank-sum test, a t-test and Spearman's correlation analysis were utilized to determine relationships between variables.
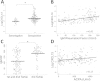
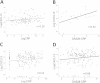
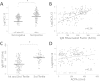
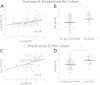
Results: In both the Dartmouth and Sherbrooke cohorts, CXCL13 levels were selectively increased in seropositive relative to seronegative RA patients (P = 0.0002 and P < 0.0001 for the respective cohorts), with a strong correlation to both immunoglobulin M (IgM) and IgA RF levels (P < 0.0001). There was a weaker relationship to ACPA titers (P = 0.03 and P = 0.006, respectively) and total IgG (P = 0.02 and P = 0.14, respectively). No relationship was seen with regard to age, sex, shared epitope status or inclusion high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) in either cohort or regarding the presence of baseline erosions in the Sherbrooke Cohort, whereas a modest relationship with Disease Activity Score in 28 joints CRP (DAS28-CRP) was seen in the Dartmouth cohort but not the Sherbrooke cohort.
Conclusion: Using both established and early RA cohorts, marked elevations of serum CXCL13 levels resided nearly completely within the seropositive population. CXCL13 levels exhibited a strong relationship with RF, whereas the association with clinical parameters (age, sex, DAS28-CRP and erosions) or other serologic markers (ACPA and IgG) was either much weaker or absent. Elevated serum CXCL13 levels may identify a subset of seropositive RA patients whose disease is shaped by or responsive to RF production.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypogalactosylation of immunoglobulin G in rheumatoid arthritis: relationship to HLA-DRB1 shared epitope, anticitrullinated protein antibodies, rheumatoid factor, and correlation with inflammatory activity.Arthritis Res Ther. 2018 Mar 14;20(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s13075-018-1540-0. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29540200 Free PMC article.
-
High serum levels of CXCL13 predict lower response to csDMARDs in both ACPA-positive and ACPA-negative early rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2025 May 1;64(5):2461-2468. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keae596. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2025. PMID: 39468732
-
Missing Anticitrullinated Protein Antibody Does Not Affect Short-term Outcomes in Early Inflammatory Arthritis: From the Canadian Early Arthritis Cohort.J Rheumatol. 2015 Nov;42(11):2023-8. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.150260. Epub 2015 Sep 1. J Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 26329342
-
Anti-carbamylated Protein Antibody Levels Correlate with Anti-Sa (Citrullinated Vimentin) Antibody Levels in Rheumatoid Arthritis.J Rheumatol. 2016 Feb;43(2):273-281. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.150179. Epub 2015 Dec 15. J Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26669911 Free PMC article.
-
Presence of Autoantibodies in Males and Females With Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Metaanalysis.J Rheumatol. 2022 Jul;49(7):663-671. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.211020. Epub 2022 Mar 15. J Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35293336
Cited by
-
Baseline CXCL10 and CXCL13 levels are predictive biomarkers for tumor necrosis factor inhibitor therapy in patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis: a pilot, prospective study.Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 Apr 22;18:93. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-0995-0. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27102921 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble markers of B cell activation suggest a role of B cells in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 29;13:954007. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.954007. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35967377 Free PMC article.
-
The role of CXCL family members in different diseases.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Jul 1;9(1):212. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01524-9. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 37393391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic review of CXCL13 as a biomarker of disease and treatment response in rheumatoid arthritis.BMC Rheumatol. 2020 Nov 2;4(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s41927-020-00154-3. BMC Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 33292827 Free PMC article.
-
CXCL13 predicts disease activity in early rheumatoid arthritis and could be an indicator of the therapeutic 'window of opportunity'.Arthritis Res Ther. 2014 Sep 24;16(5):434. doi: 10.1186/s13075-014-0434-z. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 25249397 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

