Galectin-3 is independently associated with cardiovascular mortality in community-dwelling older adults without known cardiovascular disease: The Rancho Bernardo Study
- PMID: 24766977
- PMCID: PMC4012893
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ahj.2013.12.031
Galectin-3 is independently associated with cardiovascular mortality in community-dwelling older adults without known cardiovascular disease: The Rancho Bernardo Study
Abstract
Background: Galectin-3 is a marker of myocardial fibrosis that has been implicated in the pathophysiologic pathway of fibrosis; its association with all-cause and cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality in a community-based cohort free of baseline CVD has not been reported. Our aim was to determine the association between galectin-3 levels and all-cause and CVD mortality in community-dwelling older adults without known CVD.
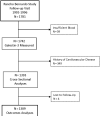
Methods: We measured plasma galectin-3 levels in 1,393 Rancho Bernardo Study participants without CVD with a mean age of 70 years. Participants were followed up for a mean of 11 years for coronary heart disease, CVD mortality, and all-cause mortality.
Results: During follow-up, 436 participants died (169 from CVD). In models adjusted for traditional CVD risk factors and renal function, galectin-3 was a significant predictor of CVD mortality (hazard ratio [HR] per SD log increase 1.30, 95% CI 1.10-1.53) and all-cause mortality (HR 1.12, 1.01-1.24), but not coronary heart disease (HR 1.09, 0.92-1.30). After further adjusting for N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide, galectin-3 remained an independent predictor (HR 1.24, 1.05-1.47) of CVD mortality. Galectin-3 improved the c statistic (0.847-0.851, P = .003) for prediction of CVD death. Net reclassification improvement (>0) with the addition of galectin-3 was 35% (P < .0001); the integrated discrimination index was also significant (P = .03). Participants with both galectin-3 and N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide above the median had increased risk of CVD death vs those with higher levels of only 1 of these markers (HR 1.74, 1.24-2.43).
Conclusion: Higher levels of galectin-3 are independently associated with all-cause and CVD mortality among community-dwelling older adults with no known CVD at baseline.
Copyright © 2014 Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is independently associated with cardiovascular disease and mortality in community-dwelling older adults: The Rancho Bernardo Study.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012 Mar 20;59(12):1101-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.11.046. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22421304 Free PMC article.
-
Growth-differentiation factor-15 is a robust, independent predictor of 11-year mortality risk in community-dwelling older adults: the Rancho Bernardo Study.Circulation. 2011 May 17;123(19):2101-10. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.979740. Epub 2011 May 2. Circulation. 2011. PMID: 21536998 Free PMC article.
-
Head-to-head comparison of 2 myocardial fibrosis biomarkers for long-term heart failure risk stratification: ST2 versus galectin-3.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014 Jan 21;63(2):158-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.07.087. Epub 2013 Sep 24. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24076531
-
Association of serum galectin-3 levels with mortality and cardiovascular disease outcomes in hemodialysis patients: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2024 Aug;56(8):2755-2767. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04026-4. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Int Urol Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38519721 Free PMC article.
-
Is simple reaction time or choice reaction time an indicator of all-cause mortality or CVD mortality?Public Health. 2021 Oct;199:34-41. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2021.07.045. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34534888 Review.
Cited by
-
Galectin-3: One Molecule for an Alphabet of Diseases, from A to Z.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 26;19(2):379. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020379. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29373564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sleep apnea and galectin-3: possible sex-specific relationship.Sleep Breath. 2019 Dec;23(4):1107-1114. doi: 10.1007/s11325-019-01788-5. Epub 2019 Feb 5. Sleep Breath. 2019. PMID: 30721387 Free PMC article.
-
GDF-15, Galectin 3, Soluble ST2, and Risk of Mortality and Cardiovascular Events in CKD.Am J Kidney Dis. 2018 Oct;72(4):519-528. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2018.03.025. Epub 2018 Jun 14. Am J Kidney Dis. 2018. PMID: 29866459 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-Specific Thresholds for Cardiac Biomarkers-We Need to Move Forward.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Mar 8;24(3):86. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2403086. eCollection 2023 Mar. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 39077486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Levels and Change in Galectin-3 and Association With Cardiovascular Events: The ARIC Study.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Jul 7;9(13):e015405. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.015405. Epub 2020 Jun 23. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 32573308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sharma UC, Pokharel S, van Brakel TJ, et al. Galectin-3 marks activated macrophages in failure-prone hypertrophied hearts and contributes to cardiac dysfunction. Circulation. 2004;110(19):3121–8. - PubMed
-
- Papaspyridonos M, McNeill E, de Bono JP, et al. Galectin-3 is an amplifier of inflammation in atherosclerotic plaque progression through macrophage activation and monocyte chemoattraction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008;28(3):433–40. - PubMed
-
- Calvier L, Miana M, Reboul P, et al. Galectin-3 mediates aldosterone-induced vascular fibrosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013;33(1):67–75. - PubMed
-
- van Kimmenade RR, Januzzi JL, Jr, Ellinor PT, et al. Utility of amino-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide, galectin-3, and apelin for the evaluation of patients with acute heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48(6):1217–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

