Neuroprotective effects of the MAO-B inhibitor, PF9601N, in an in vivo model of excitotoxicity
- PMID: 24767579
- PMCID: PMC6493024
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.12271
Neuroprotective effects of the MAO-B inhibitor, PF9601N, in an in vivo model of excitotoxicity
Abstract
Background: PF9601N [N-(2-propynyl)-2-(5-benzyloxy-indolyl) methylamine] is an inhibitor of monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B), which has shown to possess neuroprotective properties in several in vitro and in vivo models of Parkinson's disease (PD). As there is evidence that excitotoxicity may be implicated in the pathophysiology of several neurodegenerative diseases, the aim of the present work was to investigate the effects of PF9601N in an acute in vivo model of excitotoxicity induced by the local administration of kainic acid during striatal microdialysis in adult rats.
Methods: The basal and evoked release of neurotransmitters was monitored by HPLC analysis of microdialysate samples and tissue damage was evaluated histologically "ex vivo."
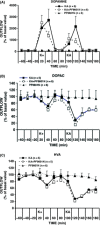
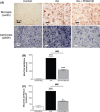
Results: PF9601N (40 mg/kg, single i.p. administration) reduced the kainate-evoked release of glutamate and aspartate and increased taurine release, but it had no effect on the release of dopamine, DOPAC, and HVA. PF9601N pretreatment also resulted in a significant reduction in the kainate-induced astrocytosis, microgliosis, and apoptosis.
Conclusions: The results suggest PF9601N to be a good candidate for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases mediated by excitotoxicity.
Keywords: Amino acids; Dopamine; Glia; Kainate; Microdialysis.
© 2014 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Novel MAO-B inhibitors: potential therapeutic use of the selective MAO-B inhibitor PF9601N in Parkinson's disease.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2011;100:217-36. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386467-3.00011-X. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21971010 Review.
-
Anti-apoptotic effect of Mao-B inhibitor PF9601N [N-(2-propynyl)-2-(5-benzyloxy-indolyl) methylamine] is mediated by p53 pathway inhibition in MPP+-treated SH-SY5Y human dopaminergic cells.J Neurochem. 2008 Jun 1;105(6):2404-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05326.x. J Neurochem. 2008. PMID: 18331475
-
Neuroprotective aspects of a novel MAO-B inhibitor PF9601N.Neurobiology (Bp). 2000;8(3-4):231-6. Neurobiology (Bp). 2000. PMID: 11225513
-
Effect of long-term treatment with selective monoamine oxidase A and B inhibitors on dopamine release from rat striatum in vivo.J Neurochem. 1996 Oct;67(4):1532-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1996.67041532.x. J Neurochem. 1996. PMID: 8858937
-
New horizons in molecular mechanisms underlying Parkinson's disease and in our understanding of the neuroprotective effects of selegiline.J Neural Transm Suppl. 1996;48:7-21. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-7494-4_2. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1996. PMID: 8988458 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioinspired Theranostic Coordination Polymer Nanoparticles for Intranasal Dopamine Replacement in Parkinson's Disease.ACS Nano. 2021 May 25;15(5):8592-8609. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c00453. Epub 2021 Apr 22. ACS Nano. 2021. PMID: 33885286 Free PMC article.
-
Isatin-based benzyloxybenzene derivatives as monoamine oxidase inhibitors with neuroprotective effect targeting neurogenerative disease treatment.RSC Adv. 2023 Dec 4;13(50):35240-35250. doi: 10.1039/d3ra07035b. eCollection 2023 Nov 30. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 38053684 Free PMC article.
-
Key Targets for Multi-Target Ligands Designed to Combat Neurodegeneration.Front Neurosci. 2016 Aug 22;10:375. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00375. eCollection 2016. Front Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27597816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic changes of five neurotransmitters and their related enzymes in various rat tissues following β-asarone and levodopa co-administration.Exp Ther Med. 2015 Oct;10(4):1566-1572. doi: 10.3892/etm.2015.2704. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Exp Ther Med. 2015. PMID: 26622527 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lau A, Tymianski M. Glutamate receptors, neurotoxicity and neurodegeneration. Pflugers Arch 2010;460:525–542. - PubMed
-
- Mattson MP. Excitotoxic and excitoprotective mechanisms: abundant targets for the prevention and treatment of neurodegenerative disorders. Neuromolecular Med 2003;3:65–94. - PubMed
-
- Nicotera P, Leist M, Ferrando‐May E. Apoptosis and necrosis: different execution of the same death. Biochem Soc Symp 1999;66:69–73. - PubMed
-
- Caudle WM, Zhang J. Glutamate, excitotoxicity and programmed cell death in Parkinson's disease. Exp Neurol 2003;220:230–233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

