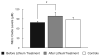Lithium increases nitric oxide levels in subjects with bipolar disorder during depressive episodes
- PMID: 24768108
- PMCID: PMC4084566
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2014.03.023
Lithium increases nitric oxide levels in subjects with bipolar disorder during depressive episodes
Abstract
Background: Altered nitric oxide (NO) signaling has been associated with the pathophysiology of Bipolar Disorder (BD), directly affecting neurotransmitter release and synaptic plasticity cascades. Lithium has shown to regulate NO levels in preclinical models. However, no study has addressed peripheral NO levels in unmedicated BD. Also, lithium's effects on NO levels have not been studied in humans.
Methods: Plasma NO was evaluated in subjects with BD I and II during a depressive episode (n = 26). Subjects had a score of ≥18 in the 21-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale and were followed-up during a 6-week trial with lithium. Plasma NO levels were also compared to matched healthy controls (n = 28). NO was determined by chemiluminescence method.
Results: Lithium treatment significantly increased plasma NO levels after 6 weeks of treatment in comparison to baseline levels in bipolar depression (p = 0.016). Baseline NO levels during depressive episodes showed no difference when matching up to healthy controls (p = 0.66).
Conclusion: The present findings suggest that lithium upregulates NO signaling in unmedicated BD with short illness duration. Further studies with larger samples are needed to confirm the effects of lithium on NO pathway and its association with synaptic plasticity and therapeutics of BD.
Keywords: Bipolar disorder; Depression; Lithium; Nitric oxide; Plasticity; Treatment.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lithium increases leukocyte mitochondrial complex I activity in bipolar disorder during depressive episodes.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015 Jan;232(1):245-50. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3655-6. Epub 2014 Jun 26. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015. PMID: 24961563
-
Lithium increases platelet serine-9 phosphorylated GSK-3β levels in drug-free bipolar disorder during depressive episodes.J Psychiatr Res. 2015 Mar;62:78-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2015.01.016. Epub 2015 Feb 7. J Psychiatr Res. 2015. PMID: 25691093
-
Oxidative stress in early stage Bipolar Disorder and the association with response to lithium.J Psychiatr Res. 2014 Mar;50:36-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2013.11.011. Epub 2013 Dec 6. J Psychiatr Res. 2014. PMID: 24332923 Free PMC article.
-
Lithium, Stress, and Resilience in Bipolar Disorder: Deciphering this key homeostatic synaptic plasticity regulator.J Affect Disord. 2018 Jun;233:92-99. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2017.12.026. Epub 2017 Dec 22. J Affect Disord. 2018. PMID: 29310970 Review.
-
[Antipsychotics in bipolar disorders].Encephale. 2004 Sep-Oct;30(5):417-24. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(04)95456-5. Encephale. 2004. PMID: 15627046 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Nitric oxide, asymmetric dimethylarginine, symmetric dimethylarginine and L-arginine levels in psychotic exacerbation of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder manic episode.Saudi Med J. 2020 Jan;41(1):38-45. doi: 10.15537/smj.2020.1.24817. Saudi Med J. 2020. PMID: 31915793 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Pathways Involved in the Rapid Antidepressant Effects of Nitrous Oxide.Biol Psychiatry. 2015 Jul 1;78(1):2-4. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.04.007. Biol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26051637 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Repeated Nitrous Oxide Exposure Exerts Antidepressant-Like Effects Through Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase Activation in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex.Front Psychiatry. 2020 Sep 3;11:837. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00837. eCollection 2020. Front Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 33088274 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Gasotransmitters in Synaptic Plasticity and Neuropsychiatric Conditions.Neural Plast. 2018 May 6;2018:1824713. doi: 10.1155/2018/1824713. eCollection 2018. Neural Plast. 2018. PMID: 29853837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum nitric oxide levels are depleted in depressed patients treated with electroconvulsive therapy.Indian J Psychiatry. 2021 Sep-Oct;63(5):456-461. doi: 10.4103/indianjpsychiatry.indianjpsychiatry_1441_20. Epub 2021 Oct 12. Indian J Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34789933 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acar G, Idiman F, Idiman E, Kirkali G, Cakmakçi H, Ozakbaş S. Nitric oxide as an activity marker in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol. 2003;250:588–92. - PubMed
-
- Anai H, Ueta Y, Serino R, Nomura M, Nakashima Y, Yamashita H. Activation of hypothalamic neuronal nitric oxide synthase in lithium-induced diabetes insipidus rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2001;26:109–20. - PubMed
-
- Andreazza AC, Kauer–Sant'anna M, Frey BN, Bond DJ, Kapczinski F, Young LT, et al. Oxidative stress markers in bipolar disorder: a meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2008;111:135–44. - PubMed
-
- Bagetta G, Corasaniti MT, Melino G, Paoletti AM, Finazzi-Agrò A, Nisticò G. Lithium and tacrine increase the expression of nitric oxide synthase mRNA in the hippocampus of rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993;197:1132–9. - PubMed
-
- Bandino A, Compagnone A, Bravoco V, Cravanzola C, Lomartire A, Rossetto C, et al. Beta-catenin triggers nuclear factor kappaB-dependent up-regulation of hepatocyte inducible nitric oxide synthase. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008;40:1861–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical