Three-year treatment outcomes in the Ahmed Baerveldt comparison study
- PMID: 24768240
- PMCID: PMC4153410
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2014.01.036
Three-year treatment outcomes in the Ahmed Baerveldt comparison study
Abstract
Purpose: To compare 3-year outcomes and complications of the Ahmed FP7 Glaucoma Valve (AGV) (New World Medical, Cucamonga, CA) and the Baerveldt Glaucoma Implant (BGI) 101-350 (Abbott Medical Optics, Abbott Park, IL) for the treatment of refractory glaucoma.
Design: Multicenter, randomized, controlled clinical trial.
Participants: A total of 276 patients: 143 in the AGV group and 133 in the BGI group.
Methods: Patients aged 18 to 85 years with refractory glaucoma and intraocular pressures (IOPs) ≥ 18 mmHg in whom an aqueous shunt was planned were randomized to an AGV or a BGI.
Main outcome measures: The IOP, visual acuity (VA), supplemental medical therapy, complications, and failure (IOP >21 mmHg or not reduced by 20% from baseline, IOP <5 mmHg, reoperation for glaucoma or removal of implant, or loss of light perception vision).
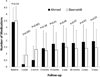
Results: At 3 years, IOP (mean ± standard deviation) was 14.3 ± ± 4.7 mmHg (AGV group) and 13.1 ± 4.5 mmHg (BGI group) (P = 0.086) on 2.0 ± 1.4 and 1.5 ± 1.4 glaucoma medications, respectively (P = 0.020). The cumulative probabilities of failure were 31.3% (standard error [SE], 4.0%) (AGV) and 32.3% (4.2%) (BGI) (P = 0.99). Postoperative complications associated with reoperation or vision loss of >2 Snellen lines occurred in 24 patients (22%) (AGV) and 38 patients (36%) (BGI) (P = 0.035). The mean change in the logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution VA at 3 years was similar (AGV: 0.21 ± 0.88, BGI: 0.26 ± 0.74) in the 2 treatment groups at 3 years (P = 0.66). The cumulative proportion of patients (SE) undergoing reoperation for glaucoma before the 3-year postoperative time point was 14.5% (3.0%) in the AGV group compared with 7.6% (2.4%) in the BGI group (P = 0.053, log rank). The relative risk of reoperation for glaucoma in the AGV group was 2.1 times that of the BGI group (95% confidence interval, 1.0-4.8; P = 0.045, Cox proportional hazards regression).
Conclusions: Implantation of the AGV was associated with the need for significantly greater adjunctive medication to achieve equal success relative to implantation of the BGI and resulted in a greater relative risk of reoperation for glaucoma. More subjects experienced serious postoperative complications in the BGI group than in the AGV group.
Copyright © 2014 American Academy of Ophthalmology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Ramulu PY, Corcoran KJ, Corcoran SL, Robin AL. Utilization of various glaucoma surgeries and procedures in Medicare beneficiaries from 1995 to 2004. Ophthalmology. 2007;114:2265–2270. - PubMed
-
- Tsai JC, Johnson CC, Dietrich MS. The Ahmed shunt versus the Baerveldt shunt for refractory glaucoma: a single-surgeon comparison of outcome. Ophthalmology. 2003;110:1814–1821. - PubMed
-
- Syed HM, Law SK, Nam SH, et al. Baerveldt-350 implant versus Ahmed valve for refractory glaucoma: a case-controlled comparison. J Glaucoma. 2004;13:38–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

