Validation of a multiplex electrochemiluminescent immunoassay platform in human and mouse samples
- PMID: 24768796
- PMCID: PMC4120713
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jim.2014.04.006
Validation of a multiplex electrochemiluminescent immunoassay platform in human and mouse samples
Abstract
Background: Despite the widespread use of multiplex immunoassays, there are very few scientific reports that test the accuracy and reliability of a platform prior to publication of experimental data. Our laboratory has previously demonstrated the need for new assay platform validation prior to use of biologic samples from large studies in order to optimize sample handling and assay performance.
Methods: In this study, our goal was to test the accuracy and reproducibility of an electrochemiluminescent multiplex immunoassay platform (Meso Scale Discovery, MSD®) and compare this platform to validated, singleplex immunoassays (R&D Systems®) using actual study subject (human plasma and mouse bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BAL) and plasma) samples.
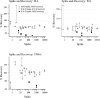
Results: We found that the MSD platform performed well on intra- and inter-assay comparisons, spike and recovery and cross-platform comparisons. The mean intra-assay CV% and range for MSD were 3.49 (0.0-10.4) for IL-6 and 2.04 (0.1-7.9) for IL-8. The correlation between values for identical samples measured on both MSD and R&D was R=0.97 for both analytes. The mouse MSD assay had a broader range of CV% with means ranging from 9.5 to 28.5 depending on the analyte. The range of mean CV% was similar for single plex ELISAs at 4.3-23.7 depending on the analyte. Regardless of species or sample type, CV% was more variable at lower protein concentrations.
Conclusions: In conclusion, we validated a multiplex electrochemiluminescent assay system and found that it has superior test characteristics in human plasma compared to mouse BALF and plasma. Both human and MSD assays compared favorably to well-validated singleplex ELISAs.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Bronchoalveolar lavage; ELISA; Immunoassay; Plasma.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures







References
-
- Belabani C, Rajasekharan S, Poupon V, Johnson T, Bar-Or A. A condensed performance-validation strategy for multiplex detection kits used in studies of human clinical samples. Journal of immunological methods. 2013;387:1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

