Follistatin-like protein 1 is a critical mediator of experimental Lyme arthritis and the humoral response to Borrelia burgdorferi infection
- PMID: 24768929
- PMCID: PMC4899828
- DOI: 10.1016/j.micpath.2014.04.005
Follistatin-like protein 1 is a critical mediator of experimental Lyme arthritis and the humoral response to Borrelia burgdorferi infection
Abstract
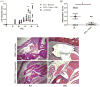
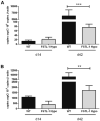
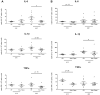
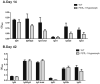
Follistatin-like protein 1 (FSTL-1) has recently been described as a critical mediator of CIA and a marker of disease activity. Lyme arthritis, caused by Borrelia burgdorferi, shares similarities with autoimmune arthritis and the experimental murine model collagen-induced arthritis (CIA). Because FSTL-1 is important in CIA and autoimmune arthritides, and Lyme arthritis shares similarities with CIA, we hypothesized that FSTL-1 may be an important mediator of Lyme arthritis. We demonstrate for the first time that FSTL-1 is induced by B. burgdorferi infection and is required for the development of Lyme arthritis in a murine model, utilizing a gene insertion to generate FSTL-1 hypomorphic mice. Using qPCR and qRT-PCR, we found that despite similar early infectious burden, FSTL-1 hypomorphic mice have improved spirochetal clearance in the face of attenuated arthritis and inflammatory cytokine production. Further, FSTL-1 mediates pathogen-specific antibody production and antigen recognition when assessed by ELISA and one- and two-dimensional immunoblotting. This study is the first to describe a role for FSTL-1 in the development of Lyme arthritis and anti-Borrelia response, and the first to demonstrate a role for FSTL-1 in response to infection, highlighting the potential for FSTL-1 as a target in the treatment of B. burgdorferi infection.
Keywords: Arthritis; Borrelia burgdorferi; FSTL-1; Lyme disease; Mouse model; humoral immunity.
Copyright © 2014. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The DBA/1 strain is a novel mouse model for experimental Borrelia burgdorferi infection.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012 Oct;19(10):1567-73. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00251-12. Epub 2012 Aug 1. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22855391 Free PMC article.
-
Dual role for Fcγ receptors in host defense and disease in Borrelia burgdorferi-infected mice.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014 Jun 11;4:75. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00075. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24967215 Free PMC article.
-
HLA-DR alleles determine responsiveness to Borrelia burgdorferi antigens in a mouse model of self-perpetuating arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2009 Dec;60(12):3831-40. doi: 10.1002/art.25005. Arthritis Rheum. 2009. PMID: 19950279 Free PMC article.
-
The role of eicosanoids in experimental Lyme arthritis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014 May 28;4:69. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00069. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24904842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Infectious arthritis and immune dysregulation: lessons from Lyme disease.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010 Jul;22(4):451-5. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e328338f73f. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010. PMID: 20375899 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Pulmonary Bacterial Immunity by Follistatin-Like Protein 1.Infect Immun. 2020 Dec 15;89(1):e00298-20. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00298-20. Print 2020 Dec 15. Infect Immun. 2020. PMID: 33077624 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of common variable immunodeficiency using embryonic stem cell therapy in a patient with lyme disease: a clinical case report.Clin Case Rep. 2018 May 2;6(6):1166-1171. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.1556. eCollection 2018 Jun. Clin Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 29881587 Free PMC article.
-
Follistatin-like protein 1 modulates IL-17 signaling via IL-17RC regulation in stromal cells.Immunol Cell Biol. 2017 Sep;95(8):656-665. doi: 10.1038/icb.2017.26. Epub 2017 Apr 5. Immunol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28377613 Free PMC article.
-
FSTL-1 Attenuation Causes Spontaneous Smoke-Resistant Pulmonary Emphysema.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020 Apr 15;201(8):934-945. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201905-0973OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 31834999 Free PMC article.
-
BB0744 Affects Tissue Tropism and Spatial Distribution of Borrelia burgdorferi.Infect Immun. 2015 Sep;83(9):3693-703. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00828-15. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 26150534 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bacon RM, Kugeler KJ, Mead PS. Surveillance for Lyme disease–United States, 1992-2006. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2008;57:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Steere AC, Malawista SE, Snydman DR, Shope RE, Andiman WA, Ross MR, et al. Lyme arthritis: an epidemic of oligoarticular arthritis in children and adults in three connecticut communities. Arthritis Rheum. 1977;20:7–17. - PubMed
-
- Harjacek M, Diaz-Cano S, Alman BA, Coburn J, Ruthazer R, Wolfe H, et al. Prominent expression of mRNA for proinflammatory cytokines in synovium in patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis or chronic Lyme arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2000;27:497–503. - PubMed
-
- McInnes IB, Schett G. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:429–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

