Follistatin-like protein 1 is a critical mediator of experimental Lyme arthritis and the humoral response to Borrelia burgdorferi infection
- PMID: 24768929
- PMCID: PMC4899828
- DOI: 10.1016/j.micpath.2014.04.005
Follistatin-like protein 1 is a critical mediator of experimental Lyme arthritis and the humoral response to Borrelia burgdorferi infection
Abstract
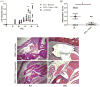
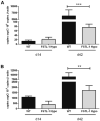
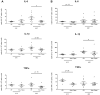
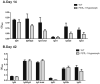
Follistatin-like protein 1 (FSTL-1) has recently been described as a critical mediator of CIA and a marker of disease activity. Lyme arthritis, caused by Borrelia burgdorferi, shares similarities with autoimmune arthritis and the experimental murine model collagen-induced arthritis (CIA). Because FSTL-1 is important in CIA and autoimmune arthritides, and Lyme arthritis shares similarities with CIA, we hypothesized that FSTL-1 may be an important mediator of Lyme arthritis. We demonstrate for the first time that FSTL-1 is induced by B. burgdorferi infection and is required for the development of Lyme arthritis in a murine model, utilizing a gene insertion to generate FSTL-1 hypomorphic mice. Using qPCR and qRT-PCR, we found that despite similar early infectious burden, FSTL-1 hypomorphic mice have improved spirochetal clearance in the face of attenuated arthritis and inflammatory cytokine production. Further, FSTL-1 mediates pathogen-specific antibody production and antigen recognition when assessed by ELISA and one- and two-dimensional immunoblotting. This study is the first to describe a role for FSTL-1 in the development of Lyme arthritis and anti-Borrelia response, and the first to demonstrate a role for FSTL-1 in response to infection, highlighting the potential for FSTL-1 as a target in the treatment of B. burgdorferi infection.
Keywords: Arthritis; Borrelia burgdorferi; FSTL-1; Lyme disease; Mouse model; humoral immunity.
Copyright © 2014. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Bacon RM, Kugeler KJ, Mead PS. Surveillance for Lyme disease–United States, 1992-2006. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2008;57:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Steere AC, Malawista SE, Snydman DR, Shope RE, Andiman WA, Ross MR, et al. Lyme arthritis: an epidemic of oligoarticular arthritis in children and adults in three connecticut communities. Arthritis Rheum. 1977;20:7–17. - PubMed
-
- Harjacek M, Diaz-Cano S, Alman BA, Coburn J, Ruthazer R, Wolfe H, et al. Prominent expression of mRNA for proinflammatory cytokines in synovium in patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis or chronic Lyme arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2000;27:497–503. - PubMed
-
- McInnes IB, Schett G. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:429–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

