Cytomegalovirus microRNAs
- PMID: 24769092
- PMCID: PMC4149926
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coviro.2014.03.015
Cytomegalovirus microRNAs
Abstract
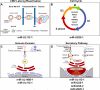
The discovery that animals, plants and DNA viruses encode microRNAs (miRNAs) has transformed our understanding of the regulation of gene expression. miRNAs are ubiquitous small non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression post-transcriptionally, generally by binding to sites within the 3' untranslated regions (UTR) of messenger RNA (mRNA) transcripts. To date, over 250 viral miRNAs have been identified primarily in members of the herpesvirus family. These viral miRNAs target both viral and cellular genes in order to regulate viral replication, the establishment and maintenance of viral latency, cell survival, and innate and adaptive immunity. This review will focus on our current knowledge of the targets and functions of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) miRNAs and their functional equivalents in other herpesviruses.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Pfeffer S, Zavolan M, Grasser FA, Chien M, Russo JJ, Ju J, John B, Enright AJ, Marks D, Sander C, et al. Identification of virus-encoded microRNAs. Science. 2004;304:734–736. The first study to identify miRNAs in a member of the herpesvirus family, EBV, using cloning and molecular biology approaches. - PubMed
-
- Pfeffer S, Sewer A, Lagos-Quintana M, Sheridan R, Sander C, Grasser FA, van Dyk LF, Ho CK, Shuman S, Chien M, et al. Identification of microRNAs of the herpesvirus family. Nat Methods. 2005;2:269–276. This study identified miRNAs expressed by several herpesviruses including KSHV, MHV68 and HCMV using bioinformatics and small RNA cloning approaches. - PubMed
-
- Grey F, Antoniewicz A, Allen E, Saugstad J, McShea A, Carrington JC, Nelson J. Identification and characterization of human cytomegalovirus-encoded microRNAs. J Virol. 2005;79:12095–12099. One of the first studies to identify and characterize HCMV miRNAs using comparative genomics, bioinformatics and molecular biology approaches. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

