Minimum requirements for accurate and efficient real-time on-chip spike sorting
- PMID: 24769170
- PMCID: PMC4151286
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2014.04.018
Minimum requirements for accurate and efficient real-time on-chip spike sorting
Abstract
Background: Extracellular recordings are performed by inserting electrodes in the brain, relaying the signals to external power-demanding devices, where spikes are detected and sorted in order to identify the firing activity of different putative neurons. A main caveat of these recordings is the necessity of wires passing through the scalp and skin in order to connect intracortical electrodes to external amplifiers. The aim of this paper is to evaluate the feasibility of an implantable platform (i.e., a chip) with the capability to wirelessly transmit the neural signals and perform real-time on-site spike sorting.
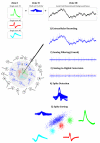
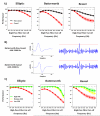
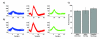
New method: We computationally modelled a two-stage implementation for online, robust, and efficient spike sorting. In the first stage, spikes are detected on-chip and streamed to an external computer where mean templates are created and sent back to the chip. In the second stage, spikes are sorted in real-time through template matching.
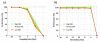
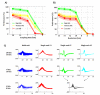
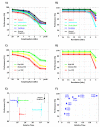
Results: We evaluated this procedure using realistic simulations of extracellular recordings and describe a set of specifications that optimise performance while keeping to a minimum the signal requirements and the complexity of the calculations.
Comparison with existing methods: A key bottleneck for the development of long-term BMIs is to find an inexpensive method for real-time spike sorting. Here, we simulated a solution to this problem that uses both offline and online processing of the data.
Conclusions: Hardware implementations of this method therefore enable low-power long-term wireless transmission of multiple site extracellular recordings, with application to wireless BMIs or closed-loop stimulation designs.
Keywords: BMIs; Extracellular recordings; On-chip; On-line; Real-time; Spike sorting; Template matching.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Abu-Nimeh FT, Aghagolzadeh M, Oweiss K. Real-time, on-chip spike sorting and firing rate estimation for cortically-controlled brain machine interface applications. 2009:39.
-
- Aghagolzadeh M, Oweiss K. An Adaptive Wireless Communication Protocol for Neural Data Transmission in Freely Behaving Subjects. 2011:404–7.
-
- Aghagolzadeh M, Zhang F, Oweiss K. An implantable VLSI architecture for real time spike sorting in cortically controlled Brain Machine Interfaces. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2010;2010:1569–1572. - PubMed
-
- Blatt M, Wiseman S, Domany E. Superparamagnetic clustering of data. Phys.Rev.Lett. 1996;76:3251–4. - PubMed
-
- Buzsaki G. Large-scale recording of neuronal ensembles. Nat.Neurosci. 2004;7:446–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

