Effect of aging on microRNAs and regulation of pathogen recognition receptors
- PMID: 24769423
- PMCID: PMC4119513
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2014.03.006
Effect of aging on microRNAs and regulation of pathogen recognition receptors
Abstract
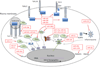
Immunosenescence is the multifactorial age-associated immune deteriorization that leads to increased susceptibility to infections and decreased responses to vaccines. Recent studies have shown a fundamental role for microRNAs (miRNAs) in regulating immune responses, and nearly all the miRNAs involved in immune regulation show modulation during aging. Aging-associated miRNAs are largely negative regulators of the immune innate response and target central nodes of aging-associated networks, in particular, NF-κB, the downstream effector of TLR signals that leads to induction of proinflammatory responses. Multiple miRNAs have been reported to share similar regulatory activity. Here we review miRNA regulation of human innate immune recognition in aging, including both activation and resolution of inflammation, critical issues in detection, and areas of active investigation into our understanding of immunosenescence.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Arnold CR, Wolf J, Brunner S, Herndler-Brandstetter D, Grubeck-Loebenstein B. Gain and loss of T cell subsets in old age--age-related reshaping of the T cell repertoire. J Clin Immunol. 2011;31:137–146. - PubMed
-
- Franceschi C, Capri M, Monti D, Giunta S, Olivieri F, Sevini F, Panourgia MP, Invidia L, Celani L, Scurti M, Cevenini E, Castellani GC, Salvioli S. Inflammaging and anti-inflammaging: a systemic perspective on aging and longevity emerged from studies in humans. Mech Ageing Dev. 2007;128:92–105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

