Degradation of Keap1 activates BH3-only proteins Bim and PUMA during hepatocyte lipoapoptosis
- PMID: 24769730
- PMCID: PMC4085536
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2014.49
Degradation of Keap1 activates BH3-only proteins Bim and PUMA during hepatocyte lipoapoptosis
Abstract
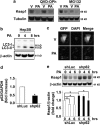
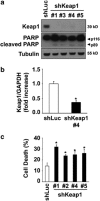
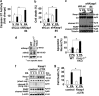
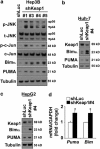
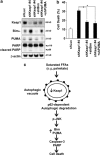
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis is characterized by hepatic steatosis, elevated levels of circulating free fatty acids (FFA) and hepatocyte lipoapoptosis. This lipoapoptosis requires increased JNK phosphorylation and activation of the pro-apoptotic BH3-only proteins Bim and PUMA. Kelch-like ECH-associated protein (Keap)-1 is a BTB/Kelch protein that can regulate the expression of Bcl-2 protein and control apoptotic cell death. Yet, the role of Keap1 in hepatocyte lipotoxicity is unclear. Here we demonstrate that Keap1 protein was rapidly degraded in hepatocytes, through autophagy in a p62-dependent manner, in response to the toxic saturated FFA palmitate, but not following incubation with the non-toxic FFA oleic acid. Stable knockdown of Keap1 expression, using shRNA technology, in hepatocarcinoma cell lines induced spontaneous cell toxicity that was associated with JNK1-dependent upregulation of Bim and PUMA protein levels. Also, Keap1 knockdown further sensitized hepatocytes to lipoapoptosis by palmitate. Likewise, primary hepatocytes isolated from liver-specific Keap1(-/-) mice displayed higher Bim and PUMA protein levels and demonstrated increased sensitivity to palmitate-induced apoptosis than wild-type mouse hepatocytes. Finally, stable knockdown of Bim or PUMA expression prevented cell toxicity induced by loss of Keap1. These results implicate p62-dependent autophagic degradation of Keap1 by palmitate as a mechanism contributing to hepatocyte lipoapoptosis.
Figures



References
-
- Angulo P, Lindor KD. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002;17 (Suppl:S186–S190. - PubMed
-
- Adams LA, Lymp JF, St, Sauver J, Sanderson SO, Lindor KD, Feldstein A, et al. The natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:113–121. - PubMed
-
- Feldstein AE, Canbay A, Angulo P, Taniai M, Burgart LJ, Lindor KD, et al. Hepatocyte apoptosis and fas expression are prominent features of human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:437–443. - PubMed
-
- Nehra V, Angulo P, Buchman AL, Lindor KD. Nutritional and metabolic considerations in the etiology of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2001;46:2347–2352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA93798/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DK081450/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK081461/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA093798/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA167708/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK057543/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01DK057543/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 07150-37/PHS HHS/United States
- P30 CA016059/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK081410/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK081450-03/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX001390/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- DK081461/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007150/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA167708/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1I01BX001390/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R55 CA093798/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

