The special case of hepatocytes: unique tissue architecture calls for a distinct mode of cell division
- PMID: 24769852
- PMCID: PMC4199811
- DOI: 10.4161/bioa.29012
The special case of hepatocytes: unique tissue architecture calls for a distinct mode of cell division
Abstract
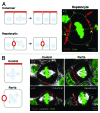
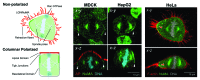
Columnar epithelia (e.g., kidney, intestine) and hepatocytes embody the two major organizational phenotypes of non-stratified epithelial cells. Columnar epithelia establish their apical and basal domains at opposing poles and organize in monolayered cysts and tubules, in which their apical surfaces form a single continuous lumen whereas hepatocytes establish their apical domains in the midst of their basolateral domains and organize a highly branched capillary luminal network, the bile canaliculi, in which a single hepatocyte can engage in lumen formation with multiple neighbors. To maintain their distinct tissue architectures, columnar epithelial cells bisect their luminal domains during symmetric cell divisions, while the cleavage furrow in dividing hepatocytes avoids bisecting the bile canalicular domains. We discuss recently discovered molecular mechanisms that underlie the different cell division phenotypes in columnar and hepatocytic model cell lines. The serine/threonine kinase Par1b determines both the epithelial lumen polarity and cell division phenotype via cell adhesion signaling that converges on the small GTPase RhoA.
Keywords: LGN/NuMA; Par1b/MARK2; RhoA; columnar and hepatocyte polarity; epithelial cells; hepatocyte polarity; mitotic spindle orientation.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
