Interaction of branch migration translocases with the Holliday junction-resolving enzyme and their implications in Holliday junction resolution
- PMID: 24770420
- PMCID: PMC4067198
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.552794
Interaction of branch migration translocases with the Holliday junction-resolving enzyme and their implications in Holliday junction resolution
Abstract
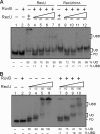
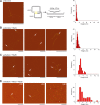
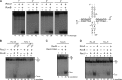
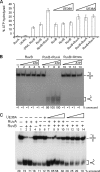
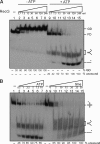
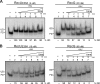
Double-strand break repair involves the formation of Holliday junction (HJ) structures that need to be resolved to promote correct replication and chromosomal segregation. The molecular mechanisms of HJ branch migration and/or resolution are poorly characterized in Firmicutes. Genetic evidence suggested that the absence of the RuvAB branch migration translocase and the RecU HJ resolvase is synthetically lethal in Bacillus subtilis, whereas a recU recG mutant was viable. In vitro RecU, which is restricted to bacteria of the Firmicutes phylum, binds HJs with high affinity. In this work we found that RecU does not bind simultaneously with RecG to a HJ. RuvB by interacting with RecU bound to the central region of HJ DNA, loses its nonspecific association with DNA, and re-localizes with RecU to form a ternary complex. RecU cannot stimulate the ATPase or branch migration activity of RuvB. The presence of RuvB·ATPγS greatly stimulates RecU-mediated HJ resolution, but the addition of ATP or RuvA abolishes this stimulatory effect. A RecU·HJ·RuvAB complex might be formed. RecU does not increase the RuvAB activities but slightly inhibits them.
Keywords: Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM); DNA Enzyme; DNA Helicase; DNA Repair; DNA-Protein Interaction; Genetic Recombination; Holliday Junction; RecG; RecU; RuvABC.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The RuvA homologues from Mycoplasma genitalium and Mycoplasma pneumoniae exhibit unique functional characteristics.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e38301. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038301. Epub 2012 May 30. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22666500 Free PMC article.
-
Activity and in vivo dynamics of Bacillus subtilis DisA are affected by RadA/Sms and by Holliday junction-processing proteins.DNA Repair (Amst). 2017 Jul;55:17-30. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2017.05.002. Epub 2017 May 5. DNA Repair (Amst). 2017. PMID: 28511132
-
DisA Restrains the Processing and Cleavage of Reversed Replication Forks by the RuvAB-RecU Resolvasome.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 20;22(21):11323. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111323. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34768753 Free PMC article.
-
Holliday junction branch migration driven by AAA+ ATPase motors.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2023 Oct;82:102650. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2023.102650. Epub 2023 Aug 19. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2023. PMID: 37604043 Review.
-
Processing of Holliday junctions by the Escherichia coli RuvA, RuvB, RuvC and RecG proteins.Experientia. 1994 Mar 15;50(3):216-22. doi: 10.1007/BF01924004. Experientia. 1994. PMID: 8143795 Review.
Cited by
-
DisA Limits RecG Activities at Stalled or Reversed Replication Forks.Cells. 2021 May 31;10(6):1357. doi: 10.3390/cells10061357. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34073022 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus subtilis RadA/Sms-Mediated Nascent Lagging-Strand Unwinding at Stalled or Reversed Forks Is a Two-Step Process: RadA/Sms Assists RecA Nucleation, and RecA Loads RadA/Sms.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 25;24(5):4536. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054536. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901969 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus subtilis PcrA Couples DNA Replication, Transcription, Recombination and Segregation.Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Jul 21;7:140. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.00140. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32793628 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus subtilis RarA Acts as a Positive RecA Accessory Protein.Front Microbiol. 2020 Feb 13;11:92. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00092. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32117122 Free PMC article.
-
Processing of stalled replication forks in Bacillus subtilis.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2024 Jan 12;48(1):fuad065. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuad065. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38052445 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mitchell A. H., West S. C. (1994) Hexameric rings of Escherichia coli RuvB protein. Cooperative assembly, processivity, and ATPase activity. J. Mol. Biol. 243, 208–215 - PubMed
-
- Fogg J. M., Schofield M. J., Déclais A. C., Lilley D. M. (2000) Yeast resolving enzyme CCE1 makes sequential cleavages in DNA junctions within the lifetime of the complex. Biochemistry 39, 4082–4089 - PubMed
-
- Ayora S., Carrasco B., Cárdenas P. P., César C. E., Cañas C., Yadav T., Marchisone C., Alonso J. C. (2011) Double-strand break repair in bacteria: a view from Bacillus subtilis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 35, 1055–1081 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

