Fractional Erbium laser in the treatment of photoaging: randomized comparative, clinical and histopathological study of ablative (2940nm) vs. non-ablative (1540nm) methods after 3 months
- PMID: 24770501
- PMCID: PMC4008055
- DOI: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20142370
Fractional Erbium laser in the treatment of photoaging: randomized comparative, clinical and histopathological study of ablative (2940nm) vs. non-ablative (1540nm) methods after 3 months
Abstract
Background: Fractional non-ablative lasers keep the epidermis intact, while fractional ablative lasers remove it, making them theoretically more effective.
Objectives: To evaluate the clinical and histological alterations induced by fractional photothermolysis for treating photoaging, comparing the possible equivalence of multiple sessions of 1540nm Erbium, to one session of 2940nm Erbium.
Methods: Eighteen patients (mean age 55.9) completed the treatment with three sessions of 1540nm fractional Erbium laser on one side of the face (50 mJ/mB, 15ms, 2 passes), and one session of 2940nm on the other side (5mJ/mB, 0.25ms, 2 passes). Biopsies were performed before and 3 months after treatment. Clinical, histological and morphometric evaluations were carried out.
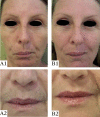
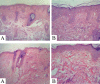
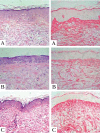
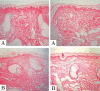
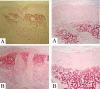
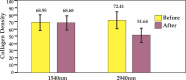
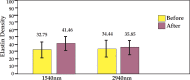
Results: All patients presented clinical improvement with no statistically significant difference (p> 0.05) between the treated sides. Histopathology revealed a new organization of collagen and elastic fibers, accompanied by edema, which was more evident with the 2940nm laser. This finding was confirmed by morphometry, which showed a decrease in collagen density for both treatments, with a statistical significance for the 2940nm laser (p > 0.001).
Conclusions: Three 1540nm sessions were clinically equivalent to one 2940nm session. The edema probably contributed to the positive results after three months, togheter with the new collagen and elastic fibers organization. The greater edema after the 2940nm session indicates that dermal remodeling takes longer than with 1540nm. It is possible that this histological superiority relates to a more prolonged effect, but a cohort longer than three months is needed to confirm that supposition.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fractional Laser Resurfacing Treats Photoaging by Promoting Neocollegenesis and Cutaneous Edema.J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020 Jan;13(1):22-27. Epub 2020 Jan 1. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 32082467 Free PMC article.
-
Study of 1550-nm Erbium glass laser fractional non-ablative treatment of photoaging: Comparative clinical effects, histopathology, electron microscopy, and immunohistochemistry.J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2016 Aug;18(4):193-203. doi: 10.3109/14764172.2015.1114645. Epub 2016 Mar 8. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2016. PMID: 26734913
-
Multiple fractional erbium: yttrium-aluminum-garnet laser sessions for upper facial rejuvenation: clinical and histological implications and expectations.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2014 Mar;13(1):30-7. doi: 10.1111/jocd.12079. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 24641603
-
Efficacy, safety, and guidelines of application of the fractional ablative laser erbium YAG 2940 nm and non-ablative laser erbium glass in rejuvenation, skin spots, and acne in different skin phototypes: a systematic review.Lasers Med Sci. 2020 Dec;35(9):1877-1888. doi: 10.1007/s10103-020-03046-7. Epub 2020 May 29. Lasers Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32472427
-
Current Status of Fractional Laser Resurfacing.JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2015 Sep-Oct;17(5):360-6. doi: 10.1001/jamafacial.2015.0693. JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2015. PMID: 26133312 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy of botulinum toxin type A injection for reducing scars in patients with forehead laceration: A double-blinded, randomized controlled study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Aug;98(34):e16952. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016952. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31441893 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of the Effectiveness of Ablative and Non-Ablative Fractional Laser Treatments for Early Stage Thyroidectomy Scars.Arch Plast Surg. 2016 Nov;43(6):575-581. doi: 10.5999/aps.2016.43.6.575. Epub 2016 Nov 18. Arch Plast Surg. 2016. PMID: 27896191 Free PMC article.
-
Fractional Laser Resurfacing Treats Photoaging by Promoting Neocollegenesis and Cutaneous Edema.J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020 Jan;13(1):22-27. Epub 2020 Jan 1. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 32082467 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Laser Effects on Skin Rejuvenation.J Lasers Med Sci. 2020 Spring;11(2):212-219. doi: 10.34172/jlms.2020.35. Epub 2020 Mar 15. J Lasers Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32273965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
White Fibrous Papulosis of the Neck Treated With Fractionated 1550-nm Erbium Glass Laser: A Case Report.J Lasers Med Sci. 2016 Fall;7(4):256-258. doi: 10.15171/jlms.2016.45. Epub 2016 Oct 27. J Lasers Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 28491262 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wells HG. The War of the Worlds. London: William Heinemann; 1898. 303 p
-
- Wheeland RG, McBurney E, Geronemus RG. The role of dermatologists in the evolution of laser surgery. Dermatol Surg. 2000;26:815–822. - PubMed
-
- Maiman TH. Biomedical lasers evolve toward clinical applications. Hosp Manage. 1966;101:39–41. - PubMed
-
- Goldman L, Wilson RG, Hornby P, Meyer RG. Radiation from Q-switched ruby laser: effect of repeated impacts of power output of 10 megawatts on a tattoo of man. J Invest Dermatol. 1965;44:69–71. - PubMed
-
- Anderson RR, Parrish JA. Selective photothermolysis: precise microsurgery by selective absorption of pulsed radiation. Science. 1983;220:524–527. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
