Antitumor activity and safety of combination therapy with the Toll-like receptor 9 agonist IMO-2055, erlotinib, and bevacizumab in advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer patients who have progressed following chemotherapy
- PMID: 24770667
- PMCID: PMC11028443
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-014-1547-6
Antitumor activity and safety of combination therapy with the Toll-like receptor 9 agonist IMO-2055, erlotinib, and bevacizumab in advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer patients who have progressed following chemotherapy
Abstract
Background: IMO-2055 is a Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) agonist that potentially enhances the efficacy of antitumor agents through immune stimulation. The objective of this phase Ib dose-escalation trial (3 + 3 design) was to determine the recommended phase II dose (RP2D) of IMO-2055 when combined with erlotinib and bevacizumab in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods: Patients with stage 3/4 NSCLC and progressive disease (PD) following chemotherapy received IMO-2055 0.08, 0.16, 0.32, or 0.48 mg/kg once weekly plus erlotinib 150 mg daily and bevacizumab 15 mg/kg every 3 weeks. Patients could receive treatment until PD or unacceptable toxicity.
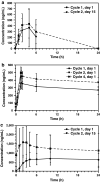
Results: Thirty-six patients were enrolled; 35 received at least one treatment dose. Two dose-limiting toxicities were observed across the dose range (Grade 3 dehydration and fatigue) with neither suggestive of a consistent toxicity pattern. IMO-2055 0.32 mg/kg was adopted as RP2D based on clinical and pharmacodynamic data. The most common treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were diarrhea (74 %), nausea (51 %), fatigue (51 %), rash (51 %), and injection-site reactions (49 %). Four patients experienced serious TEAEs considered to be study drug related. Five patients died, all due to PD. High-grade neutropenia and electrolyte disturbances previously reported with TLR9 agonists combined with platinum-based therapy were not observed in this study. Five of 33 patients evaluable for response (15 %) achieved partial response; another 20 (61 %) had stable disease, including 13 with stable disease ≥4 months.
Conclusions: IMO-2055 demonstrated good tolerability and possible antitumor activity in combination with erlotinib and bevacizumab in heavily pretreated patients with advanced NSCLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Thomas E. Boyd: Consultant to Celgene; research funding by Genentech, Celgene, GSK, Onyx and Pharmacyclics. Guillaume de La Bourdonnaye: Former employee of Merck KGaA (2008–2012). David Wages: Former employee of EMD Serono. Alice S. Bexon: Previously employee of Idera Pharmaceuticals, now paid consultant to Idera Pharmaceuticals. David A. Smith, Paul Conkling, Donald A. Richards, John J. Nemunaitis, and Alain C. Mita: None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Erlotinib alone or with bevacizumab as first-line therapy in patients with advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (JO25567): an open-label, randomised, multicentre, phase 2 study.Lancet Oncol. 2014 Oct;15(11):1236-44. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70381-X. Epub 2014 Aug 27. Lancet Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25175099 Clinical Trial.
-
Erlotinib plus bevacizumab versus erlotinib alone in patients with EGFR-positive advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (NEJ026): interim analysis of an open-label, randomised, multicentre, phase 3 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2019 May;20(5):625-635. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30035-X. Epub 2019 Apr 8. Lancet Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30975627 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase Ib trial of the Toll-like receptor 9 agonist IMO-2055 in combination with 5-fluorouracil, cisplatin, and cetuximab as first-line palliative treatment in patients with recurrent/metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.Invest New Drugs. 2013 Oct;31(5):1207-16. doi: 10.1007/s10637-013-9933-z. Epub 2013 Feb 10. Invest New Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23397499 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase I/II trial evaluating the anti-vascular endothelial growth factor monoclonal antibody bevacizumab in combination with the HER-1/epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib for patients with recurrent non-small-cell lung cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2005 Apr 10;23(11):2544-55. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.02.477. Epub 2005 Mar 7. J Clin Oncol. 2005. PMID: 15753462 Clinical Trial.
-
Open-label phase 1b study of FOLFIRI plus cetuximab plus IMO-2055 in patients with colorectal cancer who have progressed following chemotherapy for advanced or metastatic disease.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015 Apr;75(4):701-9. doi: 10.1007/s00280-015-2682-2. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25627002 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Toll-like receptor-agonist-based therapies for respiratory viral diseases: thinking outside the cell.Eur Respir Rev. 2022 May 4;31(164):210274. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0274-2021. Print 2022 Jun 30. Eur Respir Rev. 2022. PMID: 35508333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toll-Like Receptor-Based Strategies for Cancer Immunotherapy.J Immunol Res. 2021 May 22;2021:9912188. doi: 10.1155/2021/9912188. eCollection 2021. J Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 34124272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intratumoural immunotherapy: activation of nucleic acid sensing pattern recognition receptors.Immunooncol Technol. 2019 Oct 16;3:15-23. doi: 10.1016/j.iotech.2019.10.001. eCollection 2019 Oct. Immunooncol Technol. 2019. PMID: 35757301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing Cancer Therapy with Present and Emerging Immuno-Oncology Approaches.Front Oncol. 2017 Apr 18;7:64. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00064. eCollection 2017. Front Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28459041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toll-like receptor expression in human non-small cell lung carcinoma: potential prognostic indicators of disease.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 22;8(54):91860-91875. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19463. eCollection 2017 Nov 3. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29190881 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) (2012) NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines). Non-small cell lung cancer version 3. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/f_guidelines.asp. Accessed 4 Sep 2013
-
- Taxotere [product monograph] (2013) Revised Aug 2013. Bridgewater, NJ: sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2010/020449s059lbl.pdf. Accessed 16 Sep 2013
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

