Epithelial monolayer culture system for real-time single-cell analyses
- PMID: 24771696
- PMCID: PMC4001881
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.12002
Epithelial monolayer culture system for real-time single-cell analyses
Abstract
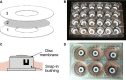
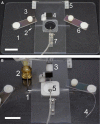
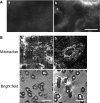
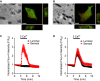
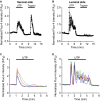
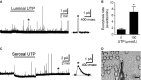
Abstract Many epithelial cells form polarized monolayers under in vivo and in vitro conditions. Typically, epithelial cells are cultured for differentiation on insert systems where cells are plated on a porous filter membrane. Although the cultured monolayers have been a standard system to study epithelial physiology, there are some limits: The epithelial cells growing inside the commercial inserts are not optimal to visualize directly through lenses on inverted microscopes. The cell images are optically distorted and background fluorescence is bright due to the filter membrane positioned between the cells and the lens. In addition, the cells are not easily accessible by electrodes due to the presence of tall side walls. Here, we present the design, fabrication, and practical applications of an improved system for analysis of polarized epithelial monolayers. This new system allows (1) direct imaging of cells without an interfering filter membrane, (2) electrophysiological measurements, and (3) detection of apical secretion with minimal dilution. Therefore, our culture method is optimized to study differentiated epithelial cells at the single-cell and subcellular levels, and can be extended to other cell types with minor modifications.
Keywords: Ca2+ signal; electrophysiology; epithelial culture; imaging; salt secretion.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Erratum: Scalable Fabrication of Stretchable, Dual Channel, Microfluidic Organ Chips.J Vis Exp. 2019 May 8;(147). doi: 10.3791/6296. J Vis Exp. 2019. PMID: 31067212
-
A modular microfluidic bioreactor with improved throughput for evaluation of polarized renal epithelial cells.Biomicrofluidics. 2016 Nov 16;10(6):064106. doi: 10.1063/1.4966986. eCollection 2016 Nov. Biomicrofluidics. 2016. PMID: 27917253 Free PMC article.
-
Hormonal responsiveness by immature rabbit uterine epithelial cells polarized in vitro.Endocrinology. 1991 Mar;128(3):1563-73. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-3-1563. Endocrinology. 1991. PMID: 1705507
-
ARPE-19, a human retinal pigment epithelial cell line with differentiated properties.Exp Eye Res. 1996 Feb;62(2):155-69. doi: 10.1006/exer.1996.0020. Exp Eye Res. 1996. PMID: 8698076
-
Epithelial cell polarization in culture: orientation of cell polarity and expression of specific functions, studied with cultured thyroid cells.J Cell Sci Suppl. 1987;8:345-58. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1987.supplement_8.19. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1987. PMID: 3332666 Review.
Cited by
-
In Pursuit of Authenticity: Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelium for Clinical Applications.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016 Nov;5(11):1562-1574. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2016-0037. Epub 2016 Jul 11. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27400791 Free PMC article.
-
Airway Surface Liquid pH Regulation in Airway Epithelium Current Understandings and Gaps in Knowledge.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 25;22(7):3384. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073384. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33806154 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Acevedo M., Steele L. W. 1993. Na+‐H+ exchanger in isolated epithelial tracheal cells from sheep. Involvement in tracheal proton secretion. Exp. Physiol.; 78:383-394 - PubMed
-
- Al‐Bazzaz F. J., Hafez N., Tyagi S., Gailey C. A., Toofanfard M., Alrefai W. A. 2001. Detection of Cl–HCO3‐ and Na+‐H+ exchangers in human airways epithelium. JOP; 2:285-290 - PubMed
-
- Bens M., Vandewalle A. 2008. Cell models for studying renal physiology. Pflugers Arch.; 457:1-15 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

