Factors associated with non-adherence to insulin in patients with type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 24772118
- PMCID: PMC3998985
Factors associated with non-adherence to insulin in patients with type 1 diabetes
Abstract
Objectives: To find out the various factors associated with non-adherence to diet, physical activity and insulin among patients with type 1 diabetes. (T1DM).
Methods: This cross sectional study was conducted among T1DM subjects attending the Baqai Institute of Diabetology & Endocrinology (BIDE) and Diabetic Association of Pakistan (DAP), from July 2011 to June 2012.Clinical characteristics, anthropometric measurements, knowledge regarding type 1 diabetes along with adherence to dietary advice, physical activity and insulin were noted on a predesigned questionnaire and score was assigned to each question. Patients were categorized as adherent or non-adherent on the basis of scores obtained. Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) for windows version 17.0 was used to analyze the data.
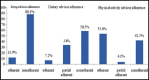
Results: A total of 194 patients (Male 94, Female 100), with mean age of 17.9± 6.4 years, mean duration of diabetes 5.37±4.96 years (38.1% >5 yrs, 61.9% <5 yrs) were included in the study. One hundred and fourteen (58.5%) patients were non adherent to dietary advice, 82(42.3%) non adherent to physical activity while 88.1% respondents were non adherent to their prescribed insulin regimen. Factors associated with non-compliance were family type, occupation & educational level of respondent's parents, duration of T1DM, family history of diabetes, frequency of visits to diabetic clinic, knowledge regarding diabetes, lack of family support and fear of hypoglycemia.
Conclusion: Non adherence to prescribed treatment regimen in patient with TIDM is quite high. There is need to design strategies to help patients and their family members understand their treatment regimen in order to improve their adherence.
Keywords: Non-adherence; Patients with type 1 diabetes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of Factors Associated With Non-Compliance to Self-Management Practices in People With Type 2 Diabetes.Cureus. 2021 Oct 20;13(10):e18918. doi: 10.7759/cureus.18918. eCollection 2021 Oct. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34826318 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with nonadherence to diet and physical activity among Nepalese type 2 diabetes patients; a cross sectional study.BMC Res Notes. 2014 Oct 24;7:758. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-7-758. BMC Res Notes. 2014. PMID: 25344089 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of barriers to the dietary adherence among type 2 diabetic patients in Pakistan: A cross-sectional study.J Pak Med Assoc. 2024 Sep;74(9):1638-1644. doi: 10.47391/JPMA.10782. J Pak Med Assoc. 2024. PMID: 39279068
-
Association of serum liver enzyme Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) in patients with type 2 diabetes.Pak J Med Sci. 2018 Jul-Aug;34(4):839-843. doi: 10.12669/pjms.344.15206. Pak J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30190738 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship of C-peptide levels to duration of Type 1 diabetes - A study from Sindh, Pakistan.Pak J Med Sci. 2020 May-Jun;36(4):765-769. doi: 10.12669/pjms.36.4.1531. Pak J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32494271 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Socio-cognitive determinants affecting insulin adherence/non-adherence in late adolescents and young adults with type 1 diabetes: a systematic review.Health Psychol Rep. 2025 Jan 31;13(1):1-26. doi: 10.5114/hpr/194439. eCollection 2025. Health Psychol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40041295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin therapy adherence and its associated factors among diabetic patients in a Ghanaian primary care hospital.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 24;20(1):e0312094. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312094. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39854487 Free PMC article.
-
Non-adherence to medication and associated factors among type 2 diabetes patients at Clinique Medicale Fraternite, Rwanda: a cross-sectional study.BMC Endocr Disord. 2022 Aug 31;22(1):219. doi: 10.1186/s12902-022-01133-0. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022. PMID: 36045370 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with non-adherence to insulin in Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in Western region of Algeria, Tlemcen: a cross-sectional study.Pan Afr Med J. 2022 Mar 3;41:172. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2022.41.172.32972. eCollection 2022. Pan Afr Med J. 2022. PMID: 35573427 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of anxiety, stress, and social support levels of female patients with type 1 diabetes and mothers whose children have type 1 diabetes.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022 Nov 5;22(1):333-340. doi: 10.1007/s40200-022-01144-7. eCollection 2023 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022. PMID: 37255808 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ciechanowski PS, Katon WJ, Russo JE, Walker EA. The patient-provider relationship: attachment theory and adherence to treatment in diabetes. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;158(1):29–35. DOI:10.1176/appi.ajp.158.1.29. - PubMed
-
- Melikian C, White TJ, Vanderplas A, Dezil CM, Chang E. Adherence to oral diabetic therapy in a managed care organizations. Clinical Therapy. 2002;24(3):460–467. DOI:10.1016/S0149-2918(02)85047-0. - PubMed
-
- Hernandez-Ronquillo L, Tellez-Zenteno JF, Garduno-Espinosa J, Gonzalez-Acevez E. Factors associated with therapy noncompliance in type 2 diabetes patients. Salud Publica de Mexico. 2003;45(3):191–197. DOI: 10.1590/S0036-36342003000300008. - PubMed
-
- Sackett LD, Haynes RB, Gordon HG, Tugwell P. Textbook of Clinical Epidemiology. London: Little, Brown and Company; 1991. pp. 249–277. DOI: 10.1002/sim.4780120211.
-
- Blanca RD, Blanca RC, Ernesto FG. Pharmacological therapy compliance in diabetes. Salud Publica de Mexico. 2001;43:233–136. DOI: org/10.1590/S0036-36342001000300009. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources