QT dispersion increases with low glomerular filtration rate in patients with coronary artery disease
- PMID: 24772124
- PMCID: PMC3998991
QT dispersion increases with low glomerular filtration rate in patients with coronary artery disease
Abstract
Objective: We aimed to evaluate the relationship between estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and QT dispersion (QTd) in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD).
Methods: Sixty patients(mean age 62.72 ± 12.48 years) included 46 male, (mean age 60.89 ± 12.70 years)and 14 female (mean age 68.71± 9.86 years) were enrolled in this study. Patients were divided into 2 groups according to their eGFR using the 6 variable MDRD equation. Group 1 consisted of patients with estimated eGFR<60 ml/min/1.73m(2) and Group 2 consisted of patients witheGFR ≥ 60 ml/min/1.73m(2).
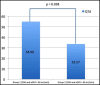
Results: Baseline patient characteristics were homogeneous in both groups except for age, gender and smoking.Also, the extent of CAD was similar in both groups (p > 0.05) QTd values were found higher in group 1 than those of group 2 (57.23 ± 40.65 ms vs. 31.23 ± 14.47 ms, p = 0.002). After adjustment for age, gender and smoking using one-way ANCOVA test, statistically significant difference in QTd still existedbetween the groups (p=0.038).
Conclusion: QTd tends to be higher in patients with poor renal function independent of severity of angiographical CAD. QTd may be a potentially useful non-invasive test in the management of patients with poor renal function, especially those with CAD.
Keywords: Coronary artery disease; Glomerular filtration rate; QT dispersion.
Figures
References
-
- Sarnak MJ, Levey AS, Schoolwerth AC, Coresh J, Culleton B, Hamm LL, et al. Kidney disease as a risk factor for development of cardiovascular disease: a statement from the American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology, and Epidemiology and Prevention. Circulation. 2003;108:2154–2169. - PubMed
-
- Brown JH, Hunt LP, Vites NP, Short CD, Gokal R, Mallick NP. Comparative mortality from cardiovascular disease in patients with chronic renal failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1994;9:1136–1142. - PubMed
-
- Garg AX, Clark WF, Haynes RB, House AA. Moderate renal insufficiency and the risk of cardiovascular mortality: results from the NHANES I. Kidney Int. 2002;61:1486–1494. - PubMed
-
- Parfrey PS, Foley RN. The clinical epidemiology of cardiac disease in chronic renal failure. J Am SocNephrol. 1999;10:1606–1615. - PubMed
-
- Lorincz I, Matyus J, Zilahi Z, Kun C, Karanyi Z, Kakuk G. QT dispersion in patients with end-stage renal failure and during hemodialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10:1297–1302. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous