Protective effect of danhong injection on acute hepatic failure induced by lipopolysaccharide and d-galactosamine in mice
- PMID: 24772178
- PMCID: PMC3977120
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/153902
Protective effect of danhong injection on acute hepatic failure induced by lipopolysaccharide and d-galactosamine in mice
Abstract
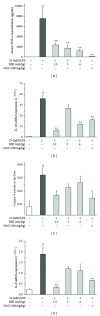
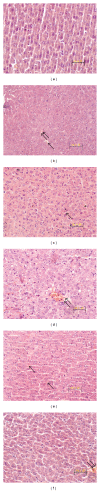
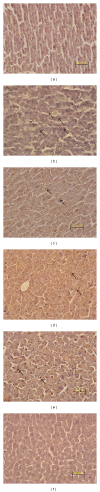
Acute hepatic failure (AHF), which leads to an extremely high mortality rate, has become the focus of attention in clinic. In this study, Danhong injection (DHI) was investigated to evaluate the preventive and protective effect on AHF induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and D-galactosamine (GalN) in mice. For AHF induction, ICR mice were intraperitoneally injected with D-GalN (700 mg/kg) and LPS (20 μ g/kg). DHI was administrated twice, at 12 and 1 h, respectively, before D-GalN/LPS injection. After stimulation with D-GalN/LPS for 1 and 6 h, serum and livers were collected for analysis. We found that mice administrated with DHI displayed a higher survival rate, lower serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), total bilirubin (TBil), glutathione S-transferase (GST), and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)- α . DHI inhibited the elevations of hepatic lipid peroxidation (malondialdehyde), caspase-8 activity, and mRNA expression levels of inflammatory cytokines (interleukin-1 β and interleukin-6) increased by D-GalN/LPS in the liver. Furthermore, liver histopathological analysis indicated that the DHI group showed markedly fewer apoptotic (TUNEL positive) cells and less pathological changes than those in the AHF model group. These results provide a novel insight into the pharmacological actions of DHI as a potential candidate for treating AHF.
Figures

References
-
- Auzinger G, Wendon J. Intensive care management of acute liver failure. Current Opinion in Critical Care. 2008;14(2):179–188. - PubMed
-
- Leifeld L, Dumoulin F-L, Purr I, et al. Early up-regulation of chemokine expression in fulminant hepatic failure. Journal of Pathology. 2003;199(3):335–344. - PubMed
-
- Diehl AM, Yin M, Fleckenstein J, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces c-jun during the regenerative response to liver injury. American Journal of Physiology. 1994;267(4):G552–G561. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

