Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Their advantages and potential clinical utility
- PMID: 24772246
- PMCID: PMC3999777
- DOI: 10.4252/wjsc.v6.i2.195
Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Their advantages and potential clinical utility
Abstract
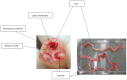
Human umbilical cord (UC) is a promising source of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Apart from their prominent advantages, such as a painless collection procedure and faster self-renewal, UC-MSCs have shown the ability to differentiate into three germ layers, to accumulate in damaged tissue or inflamed regions, to promote tissue repair, and to modulate immune response. There are diverse protocols and culture methods for the isolation of MSCs from the various compartments of UC, such as Wharton's jelly, vein, arteries, UC lining and subamnion and perivascular regions. In this review, we give a brief introduction to various compartments of UC as a source of MSCs and emphasize the potential clinical utility of UC-MSCs for regenerative medicine and immunotherapy.
Keywords: Immunotherapy; Mesenchymal stem cells; Multipotency; Umbilical cord; Wharton’s Jelly.
Figures
References
-
- Gnecchi M, Melo LG. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: isolation, expansion, characterization, viral transduction, and production of conditioned medium. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;482:281–294. - PubMed
-
- Tondreau T, Meuleman N, Delforge A, Dejeneffe M, Leroy R, Massy M, Mortier C, Bron D, Lagneaux L. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from CD133-positive cells in mobilized peripheral blood and cord blood: proliferation, Oct4 expression, and plasticity. Stem Cells. 2005;23:1105–1112. - PubMed
-
- Bieback K, Klüter H. Mesenchymal stromal cells from umbilical cord blood. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2007;2:310–323. - PubMed
-
- McElreavey KD, Irvine AI, Ennis KT, McLean WH. Isolation, culture and characterisation of fibroblast-like cells derived from the Wharton’s jelly portion of human umbilical cord. Biochem Soc Trans. 1991;19:29S. - PubMed
-
- Ishige I, Nagamura-Inoue T, Honda MJ, Harnprasopwat R, Kido M, Sugimoto M, Nakauchi H, Tojo A. Comparison of mesenchymal stem cells derived from arterial, venous, and Wharton’s jelly explants of human umbilical cord. Int J Hematol. 2009;90:261–269. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources