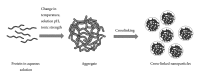
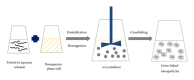
Protein nanoparticles as drug delivery carriers for cancer therapy
- PMID: 24772414
- PMCID: PMC3977416
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/180549
Protein nanoparticles as drug delivery carriers for cancer therapy
Abstract
Nanoparticles have increasingly been used for a variety of applications, most notably for the delivery of therapeutic and diagnostic agents. A large number of nanoparticle drug delivery systems have been developed for cancer treatment and various materials have been explored as drug delivery agents to improve the therapeutic efficacy and safety of anticancer drugs. Natural biomolecules such as proteins are an attractive alternative to synthetic polymers which are commonly used in drug formulations because of their safety. In general, protein nanoparticles offer a number of advantages including biocompatibility and biodegradability. They can be prepared under mild conditions without the use of toxic chemicals or organic solvents. Moreover, due to their defined primary structure, protein-based nanoparticles offer various possibilities for surface modifications including covalent attachment of drugs and targeting ligands. In this paper, we review the most significant advancements in protein nanoparticle technology and their use in drug delivery arena. We then examine the various sources of protein materials that have been used successfully for the construction of protein nanoparticles as well as their methods of preparation. Finally, we discuss the applications of protein nanoparticles in cancer therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Pathak Y. Drug Delivery Nanoparticles Formulation and Characterization. New York, NY, USA: Informa Healthcare USA; 2009. Recent developments in nanoparticulate drug delivery systems; pp. 1–7.
-
- Jahanshahi M, Zhang Z, Lyddiatt A. Subtractive chromatography for purification and recovery of nano-bioproducts. IEE Proceedings Nanobiotechnology. 2005;152(3):121–126. - PubMed
-
- Soppimath KS, Aminabhavi TM, Kulkarni AR, Rudzinski WE. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles as drug delivery devices. Journal of Controlled Release. 2001;70(1-2):1–20. - PubMed
-
- Coester C, Nayyar P, Samuel J. In vitro uptake of gelatin nanoparticles by murine dendritic cells and their intracellular localisation. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics. 2006;62(3):306–314. - PubMed
-
- Verma RK, Garg S. Current status of drug delivery technologies and future directions. Pharmaceutical Technology. 2001;25:1–14.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources