MicroRNAs: new regulators of Toll-like receptor signalling pathways
- PMID: 24772440
- PMCID: PMC3977468
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/945169
MicroRNAs: new regulators of Toll-like receptor signalling pathways
Abstract
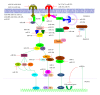
Toll-like receptors (TLRs), a critical family of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), are responsible for the innate immune responses via signalling pathways to provide effective host defence against pathogen infections. However, TLR-signalling pathways are also likely to stringently regulate tissue maintenance and homeostasis by elaborate modulatory mechanisms. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have emerged as key regulators and as an essential part of the networks involved in regulating TLR-signalling pathways. In this review, we highlight our understanding of the regulation of miRNA expression profiles by TLR-signalling pathways and the regulation of TLR-signalling pathways by miRNAs. We focus on the roles of miRNAs in regulating TLR-signalling pathways by targeting multiple molecules, including TLRs themselves, their associated signalling proteins and regulatory molecules, and transcription factors and functional cytokines induced by them, at multiple levels.
Figures
References
-
- Broz P, Monack DM. Newly described pattern recognition receptors team up against intracellular pathogens. Nature Review Immunology. 2013;13(8):551–565. - PubMed
-
- O’Neill LAJ. When signaling pathways collide: positive and negative regulation of toll-like receptor signal transduction. Immunity. 2008;29(1):12–20. - PubMed
-
- Kondo T, Kawai T, Akira S. Dissecting negative regulation of Toll-like receptor signaling. Trends in Immunology. 2012;33(9):449–458. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

