Modulation of fatty acid and bile acid metabolism by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α protects against alcoholic liver disease
- PMID: 24773203
- PMCID: PMC4047177
- DOI: 10.1111/acer.12424
Modulation of fatty acid and bile acid metabolism by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α protects against alcoholic liver disease
Abstract
Background: Chronic alcohol intake affects liver function and causes hepatic pathological changes. It has been shown that peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα)-null mice developed more pronounced hepatic changes than wild-type (WT) mice after chronic exposure to a diet containing 4% alcohol. The remarkable similarity between the histopathology of alcoholic liver disease (ALD) in Ppara-null model and in humans, and the fact that PPARα expression and activity in human liver are less than one-tenth of those in WT mouse liver make Ppara-null a good system to investigate ALD.
Methods: In this study, the Ppara-null model was used to elucidate the dynamic regulation of PPARα activity during chronic alcohol intake. Hepatic transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses were used to examine alterations of gene expression and metabolites associated with pathological changes. The changes triggered by alcohol consumption on gene expression and metabolites in Ppara-null mice were compared with those in WT mice.
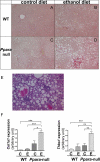
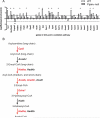
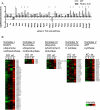
Results: The results showed that in the presence of PPARα, 3 major metabolic pathways in mitochondria, namely the fatty acid β-oxidation, the tricarboxylic acid cycle, and the electron transfer chain, were induced in response to a 2-month alcohol feeding, while these responses were greatly reduced in the absence of PPARα. In line with the transcriptional modulations of these metabolic pathways, a progressive accumulation of triglycerides, a robust increase in hepatic cholic acid and its derivatives, and a strong induction of fibrogenesis genes were observed exclusively in alcohol-fed Ppara-null mice.
Conclusions: These observations indicate that PPARα plays a protective role to enhance mitochondrial function in response to chronic alcohol consumption by adaptive transcriptional activation and suggest that activation of this nuclear receptor may be of therapeutic value in the treatment for ALD.
Keywords: Fibrogenesis; Metabolic Pathways; Metabolomics; Ppara-Null Mice; Transcriptomics.
Copyright © 2014 by the Research Society on Alcoholism.
Figures




References
-
- Aranha MM, Cortez-Pinto H, Costa A, da Silva IB, Camilo ME, de Moura MC, Rodrigues CM. Bile acid levels are increased in the liver of patients with steatohepatitis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;20:519–525. - PubMed
-
- Breitkopf K, Haas S, Wiercinska E, Singer MV, Dooley S. Anti-TGF-beta strategies for the treatment of chronic liver disease. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005a;29:121S–131S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

