The C-terminal threonine of Aβ43 nucleates toxic aggregation via structural and dynamical changes in monomers and protofibrils
- PMID: 24773532
- PMCID: PMC4030787
- DOI: 10.1021/bi500131a
The C-terminal threonine of Aβ43 nucleates toxic aggregation via structural and dynamical changes in monomers and protofibrils
Abstract
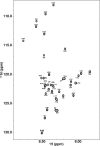
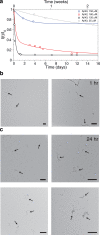
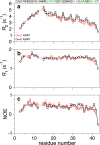
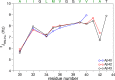
Recent studies suggest that deposition of amyloid β (Aβ) into oligomeric aggregates and fibrils, hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease, may be initiated by the aggregation of Aβ species other than the well-studied 40- and 42-residue forms, Aβ40 and Aβ42, respectively. Here we report on key structural, dynamic, and aggregation kinetic parameters of Aβ43, extended by a single threonine at the C-terminus relative to Aβ42. Using aggregation time course experiments, electron microscopy, and a combination of nuclear magnetic resonance measurements including backbone relaxation, dark-state exchange saturation transfer, and quantification of chemical shift differences and scalar coupling constants, we demonstrate that the C-terminal threonine in Aβ43 increases the rate and extent of protofibril aggregation and confers slow C-terminal motions in the monomeric and protofibril-bound forms of Aβ43. Relative to the neighboring residues, the hydrophilic Thr43 of Aβ43 favors direct contact with the protofibril surface more so than the C-terminus of Aβ40 or Aβ42. Taken together, these results demonstrate the potential of a small chemical modification to affect the properties of Aβ structure and aggregation, providing a mechanism for the potential role of Aβ43 as a primary nucleator of Aβ aggregates in Alzheimer's disease.
Figures


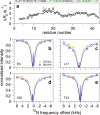

References
-
- Hardy J.; Selkoe D. J. (2002) The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 297, 353–356. - PubMed
-
- Dickson D. W.; Crystal H. A.; Bevona C.; Honer W.; Vincent I.; Davies P. (1995) Correlations of synaptic and pathological markers with cognition of the elderly. Neurobiol. Aging 16, 285–298, 298–304 (discussion). - PubMed
-
- McLean C. A.; Cherny R. A.; Fraser F. W.; Fuller S. J.; Smith M. J.; Beyreuther K.; Bush A. I.; Masters C. L. (1999) Soluble pool of Aβ amyloid as a determinant of severity of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 46, 860–866. - PubMed
-
- Walsh D. M.; Hartley D. M.; Kusumoto Y.; Fezoui Y.; Condron M. M.; Lomakin A.; Benedek G. B.; Selkoe D. J.; Teplow D. B. (1999) Amyloid β-protein fibrillogenesis. Structure and biological activity of protofibrillar intermediates. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 25945–25952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

