Combination of the ABL kinase inhibitor imatinib with the Janus kinase 2 inhibitor TG101348 for targeting residual BCR-ABL-positive cells
- PMID: 24775308
- PMCID: PMC4012544
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-8722-7-37
Combination of the ABL kinase inhibitor imatinib with the Janus kinase 2 inhibitor TG101348 for targeting residual BCR-ABL-positive cells
Abstract
Background: The ABL kinase inhibitor imatinib is highly effective in treating most, but not all, patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). This is because residual CML cells are generally present in the bone marrow microenvironment and are refractory to imatinib. Hematopoietic cytokine receptor signaling is mediated by Janus kinases (JAKs) and their downstream transcription factor, signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT). TG101348 (SAR302503) is an oral inhibitor of JAK2.
Methods: We investigated the efficacy of imatinib and TG101348 using the break point cluster region-c-Abelson (BCR-ABL)-positive cell line and primary CML samples wherein leukemia cells were protected by a feeder cell line (HS-5).
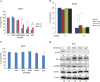
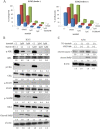
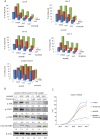
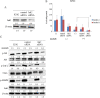
Results: Imatinib treatment resulted in partial inhibition of cell growth in HS-5-conditioned medium. Furthermore, combined treatment with imatinib and TG101348 abrogated the protective effects of HS-5-conditioned medium on K562 cells. Phosphorylation of Crk-L, a BCR-ABL substrate, decreased considerably, while apoptosis increased. In addition, the combined treatment of CD34-positive primary samples resulted in considerably increased cytotoxicity, decreased Crk-L phosphorylation, and increased apoptosis. We also investigated TG101348 activity against feeder cells and observed that STAT5 phosphorylation, granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and interleukin 6 levels decreased, indicating reduced cytokine production in HS-5 cells treated with TG101348.
Conclusions: These results showed that JAK inhibitors may enhance the cytotoxic effect of imatinib against residual CML cells and that a combined approach may be a powerful strategy against the stroma-associated drug resistance of Philadelphia chromosome-positive cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adaptive secretion of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) mediates imatinib and nilotinib resistance in BCR/ABL+ progenitors via JAK-2/STAT-5 pathway activation.Blood. 2007 Mar 1;109(5):2147-55. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-08-040022. Epub 2006 Nov 7. Blood. 2007. PMID: 17090651
-
Targeting primitive chronic myeloid leukemia cells by effective inhibition of a new AHI-1-BCR-ABL-JAK2 complex.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013 Mar 20;105(6):405-23. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djt006. Epub 2013 Feb 27. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013. PMID: 23446755 Free PMC article.
-
Selective JAK2/ABL dual inhibition therapy effectively eliminates TKI-insensitive CML stem/progenitor cells.Oncotarget. 2014 Sep 30;5(18):8637-50. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2353. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25226617 Free PMC article.
-
[Advances in basic and clinical research of flumatinib].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Jun 14;45(6):621-624. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121090-20231211-00304. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39134501 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Structure-Guided Drug Design Targeting Abl Kinase: How Structure and Regulation Can Assist in Designing New Drugs.Chembiochem. 2024 Dec 2;25(23):e202400296. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202400296. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Chembiochem. 2024. PMID: 39008807 Review.
Cited by
-
Combination Therapies in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia for Potential Treatment-Free Remission: Focus on Leukemia Stem Cells and Immune Modulation.Front Oncol. 2021 May 13;11:643382. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.643382. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34055612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal soluble factors confer imatinib drug resistance in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells.Arch Med Sci. 2020 Nov 20;17(1):266-274. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2020.101042. eCollection 2021. Arch Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 33488882 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells: targeting therapeutic implications.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Dec 18;12(1):603. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02659-1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34922630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A polymethoxyflavone from Laggera pterodonta induces apoptosis in imatinib-resistant K562R cells via activation of the intrinsic apoptosis pathway.Cancer Cell Int. 2014 Dec 5;14(1):137. doi: 10.1186/s12935-014-0137-1. eCollection 2014. Cancer Cell Int. 2014. PMID: 25530716 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNAs in leukemia drug resistance: new perspectives on molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways.Ann Hematol. 2024 May;103(5):1455-1482. doi: 10.1007/s00277-023-05383-3. Epub 2023 Aug 1. Ann Hematol. 2024. PMID: 37526673 Review.
References
-
- Sattler M, Griffin JD. Molecular mechanisms of transformation by the BCR-ABL oncogene. Semin Hematol. 2003;40(suppl 1):4–10. - PubMed
-
- Skorski T, Bellacosa A, Nieborowska-Skorska M, Majewski M, Martinez R, Choi JK, Trotta R, Wlodarski P, Perrotti D, Chan TO, Wasik MA, Tsichlis PN, Calabretta B. Transformation of hematopoietic cells by BCR/ABL requires activation of a PI-3k/Akt-dependent pathway. EMBO J. 1997;16:6151–6161. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.20.6151. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

