Health promotion interventions for increasing stroke awareness in ethnic minorities: a systematic review of the literature
- PMID: 24775404
- PMCID: PMC4019964
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-409
Health promotion interventions for increasing stroke awareness in ethnic minorities: a systematic review of the literature
Abstract
Background: Stroke places a significant burden to all affected individuals, but it is perhaps more significant amongst members of black, minority and ethnic communities, who may experience poorer awareness of stroke symptoms than the general population. Recently, several initiatives tried to improve public awareness that symptoms of stroke need to be treated as a medical emergency. However, ethnic communities present cultural barriers, requiring tailored health promotion interventions, whose effectiveness remains uncertain. Our systematic review aimed to identify relevant published evidence, synthesize the main study components and identify evidence of the effectiveness of the interventions.
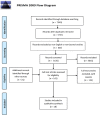
Methods: MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL, and PsycInfo were searched for journal articles on health promotion interventions for increasing stroke awareness in ethnic minorities, published in English between 1995 and 2012. Search results were collaboratively assessed by the authors; included studies were analysed to identify their main characteristics, and a thematic analysis of their content was conducted. No meta-analysis was performed, due to the heterogeneity of results.
Results: Eighteen studies were included, reporting 15 interventions conducted in the US, for African-Americans or Hispanics; populations sizes differed between interventions. Interventions were mostly carried out in community settings with different educational techniques, focussing on experiential methods. Health professionals usually organized the programs, delivered by nurses, other health professionals or volunteers.The few theory-based interventions focussed on individual-level behavioural change. Practical cultural adaptation strategies were not linked to specific theoretical frameworks. Interventions widely differed as for target populations, settings, delivery methods, contents and professional roles involved. All study designs were quantitative, and the emerging evidence of effectiveness was inconclusive.Such interventions operate in very complex scenarios, and several variables may influence their effectiveness. Therefore, qualitative or mixed-methods study designs may shed light on barriers and facilitators, experiential education strategies and community involvement.Network- and community-level theories may help improving design and evaluation of interventions.
Conclusions: Eleven case reports and four RCTs provide evidence about stroke awareness interventions organized in the US. The studies provide only partial and inconclusive evidence about the effectiveness of the interventions. Hence, further research is needed on different countries and ethnic minorities.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeted mass media interventions promoting healthy behaviours to reduce risk of non-communicable diseases in adult, ethnic minorities.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb 17;2(2):CD011683. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011683.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28211056 Free PMC article.
-
Cultural competence education for health professionals.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 May 5;2014(5):CD009405. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009405.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24793445 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for interpersonal communication about end of life care between health practitioners and affected people.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 8;7(7):CD013116. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013116.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35802350 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral interventions to reduce risk for sexual transmission of HIV among men who have sex with men.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jul 16;(3):CD001230. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001230.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. PMID: 18646068
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of computer and other electronic aids for smoking cessation: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2012;16(38):1-205, iii-v. doi: 10.3310/hta16380. Health Technol Assess. 2012. PMID: 23046909
Cited by
-
Informing Policy for Reducing Stroke Health Disparities from the Experience of African-American Male Stroke Survivors.J Racial Ethn Health Disparities. 2016 Sep;3(3):527-36. doi: 10.1007/s40615-015-0171-2. Epub 2015 Oct 20. J Racial Ethn Health Disparities. 2016. PMID: 27294742 Free PMC article.
-
Community Interventions to Increase Stroke Preparedness and Acute Stroke Treatment Rates.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2017 Nov 16;19(12):64. doi: 10.1007/s11883-017-0695-5. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2017. PMID: 29147858 Review.
-
Subjective Memory Complaints in White and African American Participants.J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 2020 May;33(3):135-143. doi: 10.1177/0891988719868305. Epub 2019 Aug 13. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 2020. PMID: 31409180 Free PMC article.
-
Stroke Disparities: Large Global Problem That Must Be Addressed.Stroke. 2015 Dec;46(12):3560-3. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.009533. Epub 2015 Oct 15. Stroke. 2015. PMID: 26470778 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Cross-Country Inequalities in Disease Burden and Quality of Care of Stroke, 1990-2021: A Systematic Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021.Eur J Neurol. 2025 Feb;32(2):e70050. doi: 10.1111/ene.70050. Eur J Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39878377 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The top 10 Causes of Death. [ http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/index.html]
-
- World Health Organization. The Global Burden of Disease: 2004 Update. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2008.
-
- Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, Bravata DM, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Franco S, Fullerton HJ, Gillespie C, Hailpern SM, Heit JA, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Kissela BM, Kittner SJ, Lackland DT, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Magid D, Marcus GM, Marelli A, Matchar DB, McGuire DK, Mohler ER, Moy CS, Mussolino ME. et al.Heart disease and stroke statistics—2013 update. A report from the American heart association. Circulation. 2013;127:e6–e245. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e31828124ad. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Prevalence and most common causes of disability among adults--United States, 2005. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009;58:421–426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical