Associations between speech features and phenotypic severity in Treacher Collins syndrome
- PMID: 24775909
- PMCID: PMC4101868
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2350-15-47
Associations between speech features and phenotypic severity in Treacher Collins syndrome
Abstract
Background: Treacher Collins syndrome (TCS, OMIM 154500) is a rare congenital disorder of craniofacial development. Characteristic hypoplastic malformations of the ears, zygomatic arch, mandible and pharynx have been described in detail. However, reports on the impact of these malformations on speech are few. Exploring speech features and investigating if speech function is related to phenotypic severity are essential for optimizing follow-up and treatment.
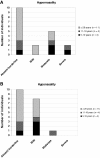
Methods: Articulation, nasal resonance, voice and intelligibility were examined in 19 individuals (5-74 years, median 34 years) divided into three groups comprising children 5-10 years (n = 4), adolescents 11-18 years (n = 4) and adults 29 years and older (n = 11). A speech composite score (0-6) was calculated to reflect the variability of speech deviations. TCS severity scores of phenotypic expression and total scores of Nordic Orofacial Test-Screening (NOT-S) measuring orofacial dysfunction were used in analyses of correlation with speech characteristics (speech composite scores).
Results: Children and adolescents presented with significantly higher speech composite scores (median 4, range 1-6) than adults (median 1, range 0-5). Nearly all children and adolescents (6/8) displayed speech deviations of articulation, nasal resonance and voice, while only three adults were identified with multiple speech aberrations. The variability of speech dysfunction in TCS was exhibited by individual combinations of speech deviations in 13/19 participants. The speech composite scores correlated with TCS severity scores and NOT-S total scores. Speech composite scores higher than 4 were associated with cleft palate. The percent of intelligible words in connected speech was significantly lower in children and adolescents (median 77%, range 31-99) than in adults (98%, range 93-100). Intelligibility of speech among the children was markedly inconsistent and clearly affecting the understandability.
Conclusions: Multiple speech deviations were identified in children, adolescents and a subgroup of adults with TCS. Only children displayed markedly reduced intelligibility. Speech was significantly correlated with phenotypic severity of TCS and orofacial dysfunction. Follow-up and treatment of speech should still be focused on young patients, but some adults with TCS seem to require continuing speech and language pathology services.
Figures
References
-
- Dauwerse JG, Dixon J, Seland S, Ruivenkamp CA, van Haeringen A, Hoefsloot LH, Peters DJ, Boers AC, Daumer-Haas C, Maiwald R, Zweier C, Kerr B, Cobo AM, Toral JF, Hoogeboom AJ, Lohmann DR, Hehr U, Dixon MJ, Breuning MH, Wieczorek D. Mutations in genes encoding subunits of RNA polymerases I and III cause Treacher Collins syndrome. Nat Genet. 2011;15:20–22. doi: 10.1038/ng.724. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources