QTL conferring fusarium crown rot resistance in the elite bread wheat variety EGA Wylie
- PMID: 24776887
- PMCID: PMC4002477
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096011
QTL conferring fusarium crown rot resistance in the elite bread wheat variety EGA Wylie
Abstract
Fusarium crown rot (FCR) is one of the most damaging cereal diseases in semi-arid regions worldwide. The genetics of FCR resistance in the bread wheat (Triticum eastivum L.) variety EGA Wylie, the most resistant commercial variety available, was studied by QTL mapping. Three populations of recombinant inbred lines were developed with this elite variety as the resistant parent. Four QTL conferring FCR resistance were detected and resistance alleles of all of them were derived from the resistant parent EGA Wylie. One of these loci was located on the short arm of chromosome 5D (designated as Qcrs.cpi-5D). This QTL explains up to 31.1% of the phenotypic variance with an LOD value of 9.6. The second locus was located on the long arm of chromosome 2D (designated as Qcrs.cpi-2D) and explained up to 20.2% of the phenotypic variance with an LOD value of 4.5. Significant effects of both Qcrs.cpi-5D and Qcrs.cpi-2D were detected in each of the three populations assessed. Another two QTL (designated as Qcrs.cpi-4B.1 and Qcrs.cpi-4B.2, respectively) were located on the short arm of chromosome 4B. These two QTL explained up to 16.9% and 18.8% of phenotypic variance, respectively. However, significant effects of Qcrs.cpi-4B.1 and Qcrs.cpi-4B.2 were not detected when the effects of plant height was accounted for by covariance analysis. The elite characteristics of this commercial variety should facilitate the incorporation of the resistance loci it contains into breeding programs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
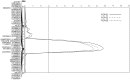

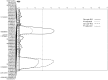
References
-
- Chakraborty S, Liu CJ, Mitter V, Scott JB, Akinsanmi OA, et al. (2006) Pathogen population structure and epidemiology are keys to wheat crown rot and Fusarium head blight management. Australasian Plant Pathology 35: 643–655.
-
- Akinsanmi OA, Mitter V, Simpfendorfer S, Backhouse D, Chakraborty S (2004) Identity and pathogenicity of Fusarium spp. isolated from wheat fields in Queensland and northern New South Wales. Crop and Pasture Science 55: 97–107.
-
- Murray GM, Brennan JP (2009) Estimating disease losses to the Australian wheat industry. Australasian Plant Pathology 38: 558–570.
-
- Smiley RW, Gourlie JA, Easley SA, Patterson L-M, Whittaker RG (2005) Crop damage estimates for crown rot of wheat and barley in the Pacific Northwest. Plant Disease 89: 595–604. - PubMed
-
- Mudge AM, Dill-Macky R, Dong Y, Gardiner DM, White RG, et al. (2006) A role for the mycotoxin deoxynivalenol in stem colonisation during crown rot disease of wheat caused by Fusarium graminearum and Fusarium pseudograminearum . Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology 69: 73–85.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

