Activation of the PI3K/mTOR/AKT pathway and survival in solid tumors: systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 24777052
- PMCID: PMC4002433
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095219
Activation of the PI3K/mTOR/AKT pathway and survival in solid tumors: systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
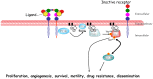
Background: Aberrations in the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)/AKT pathway are common in solid tumors. Numerous drugs have been developed to target different components of this pathway. However the prognostic value of these aberrations is unclear.
Methods: PubMed was searched for studies evaluating the association between activation of the PI3K/mTOR/AKT pathway (defined as PI3K mutation [PIK3CA], lack of phosphatase and tensin homolog [PTEN] expression by immunohistochemistry or western-blot or increased expression/activation of downstream components of the pathway by immunohistochemistry) with overall survival (OS) in solid tumors. Published data were extracted and computed into odds ratios (OR) for death at 5 years. Data were pooled using the Mantel-Haenszel random-effect model.
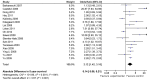
Results: Analysis included 17 studies. Activation of the PI3K/mTOR/AKT pathway was associated with significantly worse 5-year survival (OR:2.12, 95% confidence intervals 1.42-3.16, p<0.001). Loss of PTEN expression and increased expression/activation of downstream components were associated with worse survival. No association between PIK3CA mutations and survival was observed. Differences between methods for assessing activation of the PI3K/mTOR/AKT pathway were statistically significant (p = 0.04). There was no difference in the effect of up-regulation of the pathway on survival between different cancer sites (p = 0.13).
Conclusion: Activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, especially if measured by loss of PTEN expression or increased expression/activation of downstream components is associated with poor survival. PIK3CA mutational status is not associated with adverse outcome, challenging its value as a biomarker of patient outcome or as a stratification factor for patients treated with agents acting on the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Amir E, Seruga B, Martinez-Lopez J, Kwong R, Pandiella A, et al. (2011) Oncogenic targets, magnitude of benefit, and market pricing of antineoplastic drugs. J Clin Oncol 29: 2543–2549. - PubMed
-
- Slamon DJ, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S, Fuchs H, Paton V, et al. (2001) Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med 344: 783–92. - PubMed
-
- Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A, Chung HC, Shen L, et al. (2010) Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 376: 687–97. - PubMed
-
- O'Brien SG, Guilhot F, Larson RA, Gathmann I, Baccarani M, et al. (2003) Imatinib compared with interferon and low-dose cytarabine for newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 348: 994–1004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

