Detoxification treatments for opiate dependent adolescents
- PMID: 24777492
- PMCID: PMC10662542
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006749.pub3
Detoxification treatments for opiate dependent adolescents
Abstract
Background: The scientific literature examining effective treatments for opioid dependent adults clearly indicates that pharmacotherapy is a necessary and acceptable component of effective treatments for opioid dependence. Nevertheless, no studies have been published that systematically assess the effectiveness of the pharmacological detoxification among adolescents.
Objectives: To assess the effectiveness of any detoxification treatment alone or in combination with psychosocial intervention compared with no intervention, other pharmacological intervention or psychosocial interventions on completion of treatment, reducing the use of substances and improving health and social status.
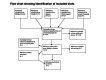
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (2014, Issue 1), PubMed (January 1966 to January 2014), EMBASE (January 1980 to January 2014), CINHAL (January 1982 to January 2014), Web of Science (1991-January 2014) and reference lists of articles.
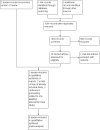
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled clinical trials comparing any pharmacological interventions alone or associated with psychosocial intervention aimed at detoxification with no intervention, placebo, other pharmacological intervention or psychosocial intervention in adolescents (13 to 18 years).
Data collection and analysis: We used standard methodological procedures recommended by The Cochrane Collaboration
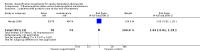
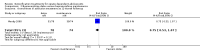
Main results: Two trials involving 190 participants were included. One trial compared buprenorphine with clonidine for detoxification. No difference was found for drop out: risk ratio (RR) 0.45 (95% confidence interval (CI): 0.20 to 1.04) and acceptability of treatment: withdrawal score mean difference (MD): 3.97 (95% CI -1.38 to 9.32). More participants in the buprenorphine group initiated naltrexone treatment: RR 11.00 (95% CI 1.58 to 76.55), quality of evidence moderate.The other trial compared maintenance treatment versus detoxification treatment: buprenorphine-naloxone maintenance versus buprenorphine detoxification. For drop out the results were in favour of maintenance treatment: RR 2.67 (95% CI 1.85, 3.86), as well as for results at follow-up RR 1.36 [95% CI 1.05to 1.76); no differences for use of opiate, quality of evidence low.
Authors' conclusions: It is difficult to draw conclusions on the basis of two trials with few participants. Furthermore, the two studies included did not consider the efficacy of methadone that is still the most frequent drug utilised for the treatment of opioid withdrawal. One possible reason for the lack of evidence could be the difficulty in conducting trials with young people due to practical and ethical reasons.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures










Update of
-
Detoxification treatments for opiate dependent adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Apr 15;(2):CD006749. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006749.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 29;(4):CD006749. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006749.pub3. PMID: 19370651 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Marsch 2005 {published data only}
-
- Marsch LA, Bickel WK, Badger GJ, Stothart ME, Quesnel KJ, Stanger C, et al. Comparison of pharmacological treatments for opioid‐dependent adolescents. Archives of General Psychiatry 2005;62(10):1157‐64. - PubMed
Woody 2008 {published data only}
References to studies excluded from this review
Baer 2007 {published data only}
-
- Baer JS, Garret SB, BeadnellB, Wells EA, Peterson PL. Brief motivational intervention with homeless adolescents: evaluating effects on substance use and service utilization. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors 2007;21(4):582‐6. - PubMed
Chakrabarti 2010 {published data only}
Ebner 2007 {published data only}
-
- Ebner R, Zierer C, Schreiber W. After detoxification is before detoxification? Long term outcome of drug dependent adolescent [Nach dem Entzug=vor demEntzug? Langzeitvrlauf bei drogenabhangigen Jugendlichen]. Psychiatrische Praxis 2007;34(Suppl 1):s42‐3.
Fiellin 2008 {published data only}
-
- Fiellin DA. Treatment of adolescent opioid dependence: no quick fix. JAMA 2008;300(17):2057‐9. - PubMed
Forcehimes 2008 {published data only}
-
- Forcehimes AA, Bogenschutz MP, Tonigan JS, Woody GE. Impacy of therapeutic alliance on treatment outcome in opioid dependent adolescent and young adult treated with buprenorphine. Proceedings of the70th Annual Scientific Meeting of the College on Problems of Drug Dependence. 2008.
Godley 2004 {published data only}
-
- Godley SH, Dennis ML, Godely MD, Funk RR. Thirty‐months relapse trajectory cluster groups among adolescents discharged from out‐patients treatment. Addiction 2004;99(Suppl 2):129‐39. - PubMed
Hill 2013 {published data only}
Kemp 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kemp R, Harris A, Vurel E, Siharthan T. Stop using stuff: trial of a drug and alcohol intervention for young people with comorbid mental illness and drug and alcohol problems. Australasian Psychiatry 2007;15(6):490‐3. - PubMed
Lehmann 1973 {published data only}
-
- Lehmann WX. The use of 1‐alpha‐acetyl‐methadol (LAAM) as compared to methadone in the maintenance and detoxification of young heroin addicts. NIDA monograph 1973;8:82‐3. - PubMed
Lloyd 1974 {published data only}
-
- Lloyd RA, Katon RN, DuPont RL. Evolution of a treatment approach for young heroin addicts. Comparison of three treatment modalities. International Journal of Addiction 1974;9(2):229‐39. - PubMed
Mannelli 2011 {published data only}
Moore 2011 {published data only}
Moore 2014 {published data only}
Mullen 2010 {published data only}
-
- Mullen L, Keenan E, Barry J, Long J, Mulholland D, Grogan L, et al. Factors predicting completion in a cohort of opiate users entering a detoxification programme. Irish Journal of Medical Science 2010;179(4):569‐73. - PubMed
Polsky 2010 {published data only}
Subramaniam 2011 {published data only}
-
- Subramaniam GA, Warden D, Minhajuddin A, Fishman MJ, Stitzer ML, Adinoff B, et al. Predictors of abstinence: National Institute of Drug Abuse multisite buprenorphine/naloxone treatment trial in opioid‐dependent youth. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2011;50(11):1120‐8. - PMC - PubMed
Warden 2012 {published data only}
References to studies awaiting assessment
Marsh 2009 {published data only}
-
- March L, Moore SK, Solhkhah R, Badger GJ. Predictors of outcome in Buprenorphine treatment for opioid‐dependent youth. Proceedings of the 71th Annual Scientific Meeting of the College on Problems of Drug Dependence; 2009 June 20‐25; Reno/Sparks, Nevada, USA. 2009.
-
- Marsch LA, MooreS, Solhkhah R. A randomized, controlled trial of buprenorphine dosing regimens for opioid dependent youth. Proceedings of the 73rd Annual Scientific Meeting of the College on Problems of Drug Dependence; 2011 June 18‐23, Hollywood, Florida. 2011.
Additional references
AIHW 2011
-
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW). Drugs in Australia 2010: tobacco, alcohol and other drugs. Drug statistics series no. 27. Cat. no. PHE 154. Canberra 2011.
Altobelli 2005
-
- Altobelli E, Rapacchietta L, Tiberti S, Petrocelli R, Cicioni L, Orio F, et al. Association between drug, alcohol and tobacco use in adolescents and socio‐familiar factors [Associazione tra l'uso di sostanze stupefacenti, alcol e tabacco negli adolescenti e contesto socio‐familiare]. Annali d'Igiene 2005;17:57‐65. - PubMed
Amato 2011
Amato 2013
Cochrane Handboook 2008
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.1 [updated September 2008]. The Cochrane Collaboration.. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org 2008.
Day 2005
EMCDDA 2012
-
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugd & Drug Addiction (EMCDDA). Annual Report: The state of the drugs problem in Europe. European Union and Norway. Office for publications of the European Communities, Luxembourg 2012.
ESPAD 2012
-
- Hibell B, Guttormsson U, Ahlström S, Balakireva O, Bjarnason T, Kokkevi A, et al. The 2011 ESPAD report: substance use among students in 36 European countries. Swedish Council for Information on Alcohol and Other Drugs, Stockholm, Sweden 2012.
Gossop 1989
-
- Gossop M, Green L, Phillips G, Bradley B. Lapse, relapse and survival among opiate addicts after treatment. British Journal of Psychiatry 1989;154:348‐53. - PubMed
Gowing 2009
-
- Gowing L, Ali R, White J. Buprenorphine for the management of opioid withdrawal. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2009, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002025.pub4] - DOI
Gowing 2009b
Gowing 2010
-
- Gowing L, Ali R, White J. Opioid antagonists under heavy sedation or anaesthesia for opioid withdrawal. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2010, Issue 1. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002022.pub3] - DOI
Gowing 2014
-
- Gowing L, Farrell M, Ali R, White J. Alpha2‐adrenergic agonists for the management of opioid withdrawal. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2014, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002024.pub4] - DOI
Hunt 1990
-
- Hunt RD, Capper L, O'Connel P. Clonidine in child and adolescent psychiatry. Journal of Child Adolescent Psychofarmacology 1990;1:87‐102. - PubMed
Kaminer 1995
-
- Kaminer Y. Pharmacotherapy for adolescents with psychoactive substance use disorders. NIDA Research Monograph 1995;156:291‐324. - PubMed
Kleber 1982
-
- Kleber HD, Riordan CE. The treatment of narcotic withdrawal: a historical review. Journal of Clinical Psichiatry 1982;43(6):30‐4. - PubMed
Levy 2007
-
- Levy S, Vaughan BL, Angulo M, Knight JR. Buprenorphine replacement therapy for adolescents with opioid dependence: early experience from a children's hospital‐based outpatient treatment program. Journal of Adolescent Health 2007;40(5):477‐82. - PubMed
Lipton 1983
-
- Lipton DS, Maranda MJ. Detoxification from heroin dependency: an overview of method and effectiveness. Advances in Alcohol and Substance Abuse 1983;2(1):31‐55.
Mattick 1996
-
- Mattick RP, Hall W. Are detoxification programmes effective?. Lancet 1996;347:97‐100. - PubMed
Monitoring the Future 2013
-
- Johnston LD, O’Malley PM, Bachman JG, Schulenberg JE. Monitoring the Future national results on drug use: 2012 Overview, Key Findings on Adolescent Drug Use. Ann Arbor: Institute for Social Research, The University of Michigan. 2013 2013.
SAMHSA 2013
-
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). Results from the 2012 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: Summary of National Findings. NSDUH Series H‐46, HHS 2013;Publication No. (SMA) 13‐4795. Rockville 2013.
Smith 2012
-
- Smith B, Fagan J, Kernan K. Outcomes of heroin dependent adolescents presenting for opiate substitution treatment. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 2012;42(1):35‐44. - PubMed
Vaillant 1988
-
- Vaillant GE. What can long‐term follow‐up teach us about relapse and prevention of relapse in addiction?. British Journal of Addiction 1988;83(10):1147‐57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

