Neamine inhibits oral cancer progression by suppressing angiogenin-mediated angiogenesis and cancer cell proliferation
- PMID: 24778013
- PMCID: PMC4757496
Neamine inhibits oral cancer progression by suppressing angiogenin-mediated angiogenesis and cancer cell proliferation
Abstract
Background: Angiogenin undergoes nuclear translocation and stimulates ribosomal RNA transcription in both endothelial and cancer cells. Consequently, angiogenin has a dual effect on cancer progression by inducing both angiogenesis and cancer cell proliferation. The aim of this study was to assess whether neamine, a blocker of nuclear translocation of angiogenin, possesses antitumor activity toward oral cancer.
Materials and methods: The antitumor effect of neamine on oral cancer cells was examined both in vitro and in vivo.
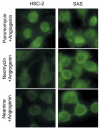
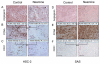
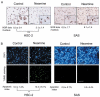
Results: Neamine inhibited the proliferation of HSC-2, but not that of SAS oral cancer cells in vitro. Treatment with neamine effectively inhibited growth of HSC-2 and SAS cell xenografts in athymic mice. Neamine treatment resulted in a significant decrease in tumor angiogenesis, accompanied by a decrease in angiogenin- and proliferating cell nuclear antigen-positive cancer cells, especially of HSC-2 tumors.
Conclusion: Neamine effectively inhibits oral cancer progression through inhibition of tumor angiogenesis. Neamine also directly inhibits proliferation of certain types of oral cancer cells. Therefore, neamine has potential as a lead compound for oral cancer therapy.
Keywords: Neamine; angiogenesis; angiogenin; cell proliferation; oral cancer.
Figures

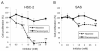

Similar articles
-
Neamine inhibits xenografic human tumor growth and angiogenesis in athymic mice.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Dec 15;11(24 Pt 1):8745-52. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1495. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16361562
-
Neamine inhibits prostate cancer growth by suppressing angiogenin-mediated rRNA transcription.Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Mar 15;15(6):1981-8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2593. Epub 2009 Mar 10. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19276260 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics of neamine in rats and anti-cervical cancer activity in vitro and in vivo.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015 Mar;75(3):465-74. doi: 10.1007/s00280-014-2658-7. Epub 2015 Jan 1. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25552400
-
Organogenesis and angiogenin.Cell Mol Life Sci. 1997 Oct;53(10):803-15. doi: 10.1007/s000180050101. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1997. PMID: 9413551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Angiogenin: involvement in angiogenesis and tumour growth].Bull Cancer. 2001 Aug;88(8):725-32. Bull Cancer. 2001. PMID: 11578940 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the Anti-Cancer Mechanisms of Antibiotics: Current Insights, Controversies, and Future Perspectives.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Dec 25;14(1):9. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14010009. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39858295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiogenin is upregulated during the alloreactive immune response and has no effect on the T-cell expansion phase, whereas it affects the contraction phase by inhibiting CD4+ T-cell apoptosis.Exp Ther Med. 2016 Nov;12(5):3471-3475. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3786. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Exp Ther Med. 2016. PMID: 27882181 Free PMC article.
-
Neamine is preferential as an anti-prostate cancer reagent by inhibiting cell proliferation and angiogenesis, with lower toxicity than cis-platinum.Oncol Lett. 2015 Jul;10(1):137-142. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.3227. Epub 2015 May 19. Oncol Lett. 2015. PMID: 26170989 Free PMC article.
-
Angiogenin negatively regulates the expression of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and inhibits bFGF promoter activity.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018 Jul 1;11(7):3277-3285. eCollection 2018. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018. PMID: 31949702 Free PMC article.
-
Neamine inhibits growth of pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in vivo.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2016 Feb;36(1):82-87. doi: 10.1007/s11596-016-1546-2. Epub 2016 Feb 3. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 26838745
References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. - PubMed
-
- Hasina R, Lingen MW. Angiogenesis in oral cancer. J Dent Educ. 2001;65:1282–1290. - PubMed
-
- Xu ZP, Tsuji T, Riordan JF, Hu GF. The nuclear function of angiogenin in endothelial cells is related to rRNA production. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;294:287–292. - PubMed
-
- Tsuji T, Sun Y, Kishimoto K, Olson KA, Liu S, Hirukawa S, Hu GF. Angiogenin is translocated to the nucleus of HeLa cells and is involved in ribosomal RNA transcription and cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2005;65:1352–1360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
