Neurosteroids promote phosphorylation and membrane insertion of extrasynaptic GABAA receptors
- PMID: 24778259
- PMCID: PMC4024867
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1403285111
Neurosteroids promote phosphorylation and membrane insertion of extrasynaptic GABAA receptors
Abstract
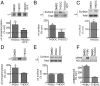
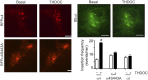
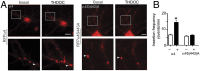
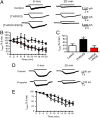
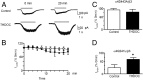
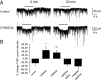
Neurosteroids are synthesized within the brain and act as endogenous anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, hypnotic, and sedative agents, actions that are principally mediated via their ability to potentiate phasic and tonic inhibitory neurotransmission mediated by γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors (GABAARs). Although neurosteroids are accepted allosteric modulators of GABAARs, here we reveal they exert sustained effects on GABAergic inhibition by selectively enhancing the trafficking of GABAARs that mediate tonic inhibition. We demonstrate that neurosteroids potentiate the protein kinase C-dependent phosphorylation of S443 within α4 subunits, a component of GABAAR subtypes that mediate tonic inhibition in many brain regions. This process enhances insertion of α4 subunit-containing GABAAR subtypes into the membrane, resulting in a selective and sustained elevation in the efficacy of tonic inhibition. Therefore, the ability of neurosteroids to modulate the phosphorylation and membrane insertion of α4 subunit-containing GABAARs may underlie the profound effects these endogenous signaling molecules have on neuronal excitability and behavior.
Keywords: PKC; current rundown; receptor insertion; tonic current.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Belelli D, Lambert JJ. Neurosteroids: Endogenous regulators of the GABA(A) receptor. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6(7):565–575. - PubMed
-
- Paul SM, Purdy RH. Neuroactive steroids. FASEB J. 1992;6(6):2311–2322. - PubMed
-
- Crawley JN, Glowa JR, Majewska MD, Paul SM. Anxiolytic activity of an endogenous adrenal steroid. Brain Res. 1986;398(2):382–385. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NS056359/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH097446/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- NS051195/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS051195/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS054900/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MH097446/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS056359/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS047478/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS073574/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS048045/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH118263/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS102937/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS081986/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS081735/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS061764/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

