Location of maxillary intraosseous vascular anastomosis based on the tooth position and height of the residual alveolar bone: computed tomographic analysis
- PMID: 24778898
- PMCID: PMC3999352
- DOI: 10.5051/jpis.2014.44.2.50
Location of maxillary intraosseous vascular anastomosis based on the tooth position and height of the residual alveolar bone: computed tomographic analysis
Abstract
Purpose: The aims of this study were to measure the distance of the intraosseous vascular anastomosis in the anterolateral wall of the maxillary sinus from different reference points, and to correlate the location of the intraosseous vascular anastomosis with the tooth position and the residual bone height of the maxilla.
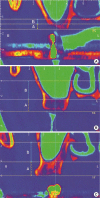
Methods: Computed tomography (CT) images were taken from 283 patients undergoing dental implants placement in the posterior maxilla. Three horizontal lines were drawn at the ridge crest, maxillary sinus floor, and the position of the anastomosis. A vertical second line at the center of each tooth was drawn perpendicular to the horizontal lines. The distance from the ridge crest to the maxillary sinus floor and the distance from the maxillary sinus floor to the bony canal were measured from the intersections of the horizontal and vertical lines. The residual alveolar bone height was used to categorize three groups: group 1,<4 mm; group 2, between 4 and 8 mm; and group 3, >8 mm.
Results: The residual bone height values of different tooth positions were significantly different (P=0.0002). The distance from the maxillary sinus floor to the intraosseous vascular anastomosis was significantly different between groups 1 and 3 (P=0.0039). At the molar sites, a moderate negative correlation was found between the residual bone height and the distance from the maxillary sinus floor to the intraosseous anastomosis. The distances of the alveolar ridge crest and the maxillary sinus from the intraosseous vascular anastomosis were not significantly different between sexes.
Conclusions: Within the limitations of this study, sites with a higher residual bone height in the molar regions were at a relatively high risk of artery damage during window osteotomy preparation; therefore, we recommend taking more precautions when using a lateral approach for sinus elevation.
Keywords: Alveolar bone loss; Edentulous mouth; Maxillary artery; Sinus floor augmentation; X-ray computed tomography.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Measurement of the height and width of residual alveolar crests in low-set maxillary sinus patients with missing upper molar].Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2011 Jun;20(3):308-13. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2011. PMID: 21779744 Chinese.
-
Cone Beam CT Evaluation of Maxillary Sinus Floor and Alveolar Crest Anatomy for the Safe Placement of Implants.Curr Med Imaging. 2020;16(7):913-920. doi: 10.2174/1573405615666191212105745. Curr Med Imaging. 2020. PMID: 33059561
-
Radiographic study of the distribution of maxillary intraosseous vascular canal in Koreans.Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016 Jan 4;38(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s40902-015-0045-x. eCollection 2016 Dec. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016. PMID: 26767186 Free PMC article.
-
[Topographic assessment of the vascular anastomosis in the maxillary sinus wall using cone-beam computed tomography].Stomatologiia (Mosk). 2022;101(1):60-65. doi: 10.17116/stomat202210101160. Stomatologiia (Mosk). 2022. PMID: 35184535 Russian.
-
Prevalence and morphometric analysis of the alveolar antral artery in a group of Thai population by cone beam computed tomography.Oral Radiol. 2021 Jul;37(3):452-462. doi: 10.1007/s11282-020-00478-3. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Oral Radiol. 2021. PMID: 32852656
Cited by
-
Morphometric Analysis of the Maxillary Sinus and Its Implications for Sinus Augmentation Surgery in an Eastern Indian Population.Cureus. 2025 Jul 13;17(7):e87809. doi: 10.7759/cureus.87809. eCollection 2025 Jul. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40799863 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic detection of posterior superior alveolar artery in dental cone-beam CT images using a deeply supervised multi-scale 3D network.Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2024 Jan 11;53(1):22-31. doi: 10.1093/dmfr/twad002. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38214942 Free PMC article.
-
Anatomy of the Posterior Superior Alveolar Artery: a Cone-Beam Computed Tomographic Study.J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2022 Mar;21(1):203-210. doi: 10.1007/s12663-020-01386-z. Epub 2020 Jun 3. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2022. PMID: 35400914 Free PMC article.
-
Distance of the alveolar antral artery from the alveolar crest. Related factors and surgical considerations in sinus floor elevation.Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2016 Nov 1;21(6):e758-e765. doi: 10.4317/medoral.21475. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2016. PMID: 27694790 Free PMC article.
-
Association of location and diameter of alveolar antral artery to crest of alveolar bone in dentate and partially edentulous patients - A cone-beam computed tomography study.J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2021 Jan-Feb;25(1):55-60. doi: 10.4103/jisp.jisp_603_19. Epub 2020 Sep 21. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2021. PMID: 33642742 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Garg AK, Quinones CR. Augmentation of the maxillary sinus: a surgical technique. Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent. 1997;9:211–219. - PubMed
-
- Wallace SS, Froum SJ. Effect of maxillary sinus augmentation on the survival of endosseous dental implants: a systematic review. Ann Periodontol. 2003;8:328–343. - PubMed
-
- Flanagan D. Arterial supply of maxillary sinus and potential for bleeding complication during lateral approach sinus elevation. Implant Dent. 2005;14:336–338. - PubMed
-
- Rosano G, Taschieri S, Gaudy JF, Del Fabbro M. Maxillary sinus vascularization: a cadaveric study. J Craniofac Surg. 2009;20:940–943. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

