Deep sequencing strategies for mapping and identifying mutations from genetic screens
- PMID: 24778934
- PMCID: PMC3875646
- DOI: 10.4161/worm.25081
Deep sequencing strategies for mapping and identifying mutations from genetic screens
Abstract
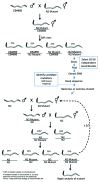
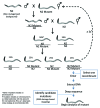
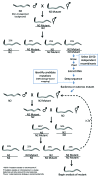
The development of next-generation sequencing technologies has enabled rapid and cost effective whole genome sequencing. This technology has allowed researchers to shortcut time-consuming and laborious methods used to identify nucleotide mutations in forward genetic screens in model organisms. However, causal mutations must still be mapped to a region of the genome so as to aid in their identification. This can be achieved simultaneously with deep sequencing through various methods. Here we discuss alternative deep sequencing strategies for simultaneously mapping and identifying causal mutations in Caenorhabditis elegans from mutagenesis screens. Focusing on practical considerations, such as the particular mutant phenotype obtained, this review aims to aid the reader in choosing which strategy to adopt to successfully clone their mutant.
Keywords: C. elegans; EMS; NGS; SNP mapping; WGS; deep sequencing; forward genetics; genetic mapping; next-generation sequencing; whole genome sequencing.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Approaches for Mutation Mapping and Identification in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2016 Oct;204(2):451-474. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.186197. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 27729495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Next-Generation Sequencing for Identification of EMS-Induced Mutations in Caenorhabditis elegans.Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2017 Jan 5;117:7.29.1-7.29.12. doi: 10.1002/cpmb.27. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28060408 Free PMC article.
-
Whole genome sequencing and the transformation of C. elegans forward genetics.Methods. 2014 Aug 1;68(3):437-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2014.05.008. Epub 2014 May 27. Methods. 2014. PMID: 24874788
-
A machine learning enhanced EMS mutagenesis probability map for efficient identification of causal mutations in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS Genet. 2024 Aug 26;20(8):e1011377. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011377. eCollection 2024 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 39186782 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives for identification of mutations in the zebrafish: making use of next-generation sequencing technologies for forward genetic approaches.Methods. 2013 Aug 15;62(3):185-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2013.05.015. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Methods. 2013. PMID: 23748111 Review.
Cited by
-
Fast forward genetics to identify mutations causing a high light tolerant phenotype in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by whole-genome-sequencing.BMC Genomics. 2015 Feb 6;16(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1232-y. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25730202 Free PMC article.
-
Using C. elegans Forward and Reverse Genetics to Identify New Compounds with Anthelmintic Activity.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016 Oct 18;10(10):e0005058. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005058. eCollection 2016 Oct. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016. PMID: 27755544 Free PMC article.
-
Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Approaches for Mutation Mapping and Identification in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2016 Oct;204(2):451-474. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.186197. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 27729495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kendomycin Cytotoxicity against Bacterial, Fungal, and Mammalian Cells Is Due to Cation Chelation.J Nat Prod. 2020 Apr 24;83(4):965-971. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b00826. Epub 2020 Mar 17. J Nat Prod. 2020. PMID: 32182062 Free PMC article.
-
Next-Generation Sequencing for Identification of EMS-Induced Mutations in Caenorhabditis elegans.Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2017 Jan 5;117:7.29.1-7.29.12. doi: 10.1002/cpmb.27. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28060408 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
