Comparison of routine laboratory measures of heparin anticoagulation for neonates on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
- PMID: 24779122
- PMCID: PMC4557514
Comparison of routine laboratory measures of heparin anticoagulation for neonates on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
Abstract
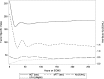
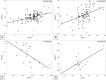
Our objective was to determine the best measure of heparin anticoagulation in neonatal patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Activated clotting time (ACT), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), and antifactor Xa levels, along with corresponding heparin infusion rates and heparin bolus volumes, were collected from neonates receiving ECMO at our institution from 2008 to 2013. After natural log transformation of antifactor Xa, ACT, and aPTT, overall correlations between antifactor Xa levels and either ACT or aPTT and correlations between these tests and heparin infusion rates were evaluated using linear mixed models that accounted for both within- and between-patient correlations. Twenty-six neonates with an average weight of 3.4 kg (standard deviation .7) had a total of 27 separate ECMO runs during the study period. Within each patient, ACT (r = .40, p < .0001) and aPTT (r = .48, p < .0001) were both directly correlated with antifactor Xa levels. In contrast, between patients, only aPTT maintained a direct correlation with antifactor Xa (r = .61, p = .07), whereas ACT showed a statistically significant inverse correlation with antifactor Xa (r = -.48, p = .04). Compared with ACT, aPTT is more consistently reflective of the anticoagulation status both within each patient on ECMO and between patients treated with ECMO. Future efforts to develop standardized heparin infusion algorithms for patients on ECMO should consider using aPTT levels to monitor anticoagulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The senior author has stated that the authors have reported no material, financial, or other relationship with any healthcare-related business or other entity whose products or services are discussed in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Oliver WC.. Anticoagulation and coagulation management for ECMO. Semin Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2009;13:154–175. - PubMed
-
- Hirsh J, Warkentin TE, Shaughnessy SG, et al. . Heparin and low-molecular-weight heparin: Mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, dosing, monitoring, efficacy, and safety. Chest. 2001;119(Suppl):64S–94S. - PubMed
-
- Smythe MA, Caffee A.. Anticoagulation monitoring. Journal of Pharmacy Practice. 2004;17:317–326.
-
- Srinivasan D, Watzak B.. Anticoagulant use in real time. J Pharm Pract. 2013;26:270–279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
