Taking the temperature of the interiors of magnetically heated nanoparticles
- PMID: 24779552
- PMCID: PMC4046777
- DOI: 10.1021/nn501250e
Taking the temperature of the interiors of magnetically heated nanoparticles
Abstract
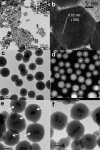
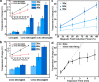
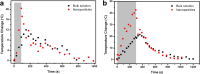
The temperature increase inside mesoporous silica nanoparticles induced by encapsulated smaller superparamagnetic nanocrystals in an oscillating magnetic field is measured using a crystalline optical nanothermometer. The detection mechanism is based on the temperature-dependent intensity ratio of two luminescence bands in the upconversion emission spectrum of NaYF4:Yb(3+), Er(3+). A facile stepwise phase transfer method is developed to construct a dual-core mesoporous silica nanoparticle that contains both a nanoheater and a nanothermometer in its interior. The magnetically induced heating inside the nanoparticles varies with different experimental conditions, including the magnetic field induction power, the exposure time to the magnetic field, and the magnetic nanocrystal size. The temperature increase of the immediate nanoenvironment around the magnetic nanocrystals is monitored continuously during the magnetic oscillating field exposure. The interior of the nanoparticles becomes much hotter than the macroscopic solution and cools to the temperature of the ambient fluid on a time scale of seconds after the magnetic field is turned off. This continuous absolute temperature detection method offers quantitative insight into the nanoenvironment around magnetic materials and opens a path for optimizing local temperature controls for physical and biomedical applications.
Figures


References
-
- Rosensweig R. E. Heating Magnetic Fluid with Alternating Magnetic Field. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 252, 370–374.
-
- Hergt R.; Dutz S.; Mueller R.; Zeisberger M. Magnetic Particle Hyperthermia: Nanoparticle Magnetism and Materials Development for Cancer Therapy. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 2006, 18, S2919–S2934.
-
- Etheridge M. L.; Bischof J. C. Optimizing Magnetic Nanoparticle Based Thermal Therapies within the Physical Limits of Heating. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 41, 78–88. - PubMed
-
- Kim J.; Kim H. S.; Lee N.; Kim T.; Kim H.; Yu T.; Song I. C.; Moon W. K.; Hyeon T. Multifunctional Uniform Nanoparticles Composed of a Magnetite Nanocrystal Core and a Mesoporous Silica Shell for Magnetic Resonance and Fluorescence Imaging and for Drug Delivery. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 8438–8441. - PubMed
-
- Lu A.-H.; Salabas E. L.; Schueth F. Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Protection, Functionalization, and Application. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1222–1244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

