Redox potential ultrasensitive nanoparticle for the targeted delivery of camptothecin to HER2-positive cancer cells
- PMID: 24779647
- PMCID: PMC4334268
- DOI: 10.1021/mp5000482
Redox potential ultrasensitive nanoparticle for the targeted delivery of camptothecin to HER2-positive cancer cells
Abstract
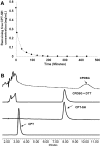
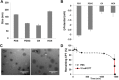
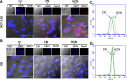
Ideal "smart" nanoparticles for drug delivery should enhance therapeutic efficacy without introducing side effects. To achieve that, we developed a drug delivery system (HCN) based on a polymer-drug conjugate of poly[2-(pyridin-2-yldisulfanyl)]-graft-poly(ethylene glycol) and camptothecin with an intracellularly cleavable linker and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) targeting ligands. An in vitro drug release study found that HCN was stable in the physiological environment and supersensitive to the stimulus of elevated intracellular redox potential, releasing all payloads in less than 30 min. Furthermore, confocal microscopy revealed that HCN could specifically enter HER2-positive cancer cells. As a consequence, HCN could effectively kill HER2-positive cancer cells while not affecting HER2-negative cells.
Figures



References
-
- Master A. M.; Rodriguez M. E.; Kenney M. E.; Oleinick N. L.; Gupta A. S. Delivery of the photosensitizer Pc 4 in PEG-PCL micelles for in vitro PDT studies. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 9952386–2398. - PubMed
-
- Moreira J. N.; Gaspar R.; Allen T. M. Targeting stealth liposomes in a murine model of human small cell lung cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 15152167–176. - PubMed
-
- Shi M.; Ho K.; Keating A.; Shoichet M. S. Doxorubicin-Conjugated Immuno-Nanoparticles for Intracellular Anticancer Drug Delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19111689–1696.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

