The stem cell adjuvant with Exendin-4 repairs the heart after myocardial infarction via STAT3 activation
- PMID: 24779911
- PMCID: PMC4124022
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.12272
The stem cell adjuvant with Exendin-4 repairs the heart after myocardial infarction via STAT3 activation
Abstract
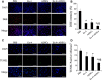
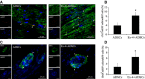
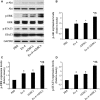
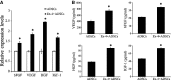
The poor survival of cells in ischaemic myocardium is a major obstacle for stem cell therapy. Exendin-4 holds the potential of cardioprotective effect based on its pleiotropic activity. This study investigated whether Exendin-4 in conjunction with adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) could improve the stem cell survival and contribute to myocardial repairs after infarction. Myocardial infarction (MI) was induced by the left anterior descending artery ligation in adult male Sprague-Dawley rats. ADSCs carrying double-fusion reporter gene [firefly luciferase and monomeric red fluorescent protein (fluc-mRFP)] were quickly injected into border zone of MI in rats treated with or without Exendin-4. Exendin-4 enhanced the survival of transplanted ADSCs, as demonstrated by the longitudinal in vivo bioluminescence imaging. Moreover, ADSCs adjuvant with Exendin-4 decreased oxidative stress, apoptosis and fibrosis. They also improved myocardial viability and cardiac function and increased the differentiation rates of ADSCs into cardiomyocytes and vascular smooth muscle cells in vivo. Then, ADSCs were exposed to hydrogen peroxide/serum deprivation (H(2)O(2)/SD) to mimic the ischaemic environment in vitro. Results showed that Exendin-4 decreased the apoptosis and enhanced the paracrine effect of ADSCs. In addition, Exendin-4 activated signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 (STAT3) through the phosphorylation of Akt and ERK1/2. Furthermore, Exendin-4 increased the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2, but decreased the pro-apoptotic protein Bax of ADSCs. In conclusion, Exendin-4 could improve the survival and therapeutic efficacy of transplanted ADSCs through STAT3 activation via the phosphorylation of Akt and ERK1/2. This study suggests the potential application of Exendin-4 for stem cell-based heart regeneration.
Keywords: Exendin-4; STAT3; adipose-derived stem cell; myocardial infarction; paracrine.
© 2014 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Exendin-4 pretreated adipose derived stem cells are resistant to oxidative stress and improve cardiac performance via enhanced adhesion in the infarcted heart.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 10;9(6):e99756. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099756. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24915574 Free PMC article.
-
Exendin-4 enhances the migration of adipose-derived stem cells to neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocyte-derived conditioned medium via the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt-stromal cell-derived factor-1α/CXC chemokine receptor 4 pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Jun;11(6):4063-72. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3243. Epub 2015 Jan 22. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25625935 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of mesenchymal stem cell injection with icariin for the treatment of diabetes-associated erectile dysfunction.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 28;12(3):e0174145. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174145. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28350842 Free PMC article.
-
A brief review: adipose-derived stem cells and their therapeutic potential in cardiovascular diseases.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017 Jun 5;8(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0585-3. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28583198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies for improving adipose-derived stem cells for tissue regeneration.Burns Trauma. 2022 Aug 16;10:tkac028. doi: 10.1093/burnst/tkac028. eCollection 2022. Burns Trauma. 2022. PMID: 35992369 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exendin-4 promotes proliferation of adipose-derived stem cells through ERK and JNK signaling pathways.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2016 May;52(5):598-606. doi: 10.1007/s11626-016-0003-7. Epub 2016 Mar 1. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2016. PMID: 26932601
-
Preconditioning c-Kit-positive Human Cardiac Stem Cells with a Nitric Oxide Donor Enhances Cell Survival through Activation of Survival Signaling Pathways.J Biol Chem. 2016 Apr 29;291(18):9733-47. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.687806. Epub 2016 Mar 3. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26940876 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory and Antioxidative potentials of adipose-derived Mesenchymal stem cells isolated from breast versus abdominal tissue: a comparative study.Cell Regen. 2020 Oct 6;9(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s13619-020-00056-2. Cell Regen. 2020. PMID: 33020894 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effect Of Vasicine Against Myocardial Infarction In Rats Via Modulation Of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, And The PI3K/Akt Pathway.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Oct 31;13:3773-3784. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S220396. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31802850 Free PMC article.
-
Analyzing Impetus of Regenerative Cellular Therapeutics in Myocardial Infarction.J Clin Med. 2020 Apr 28;9(5):1277. doi: 10.3390/jcm9051277. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32354170 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Segers VF, Lee RT. Stem-cell therapy for cardiac disease. Nature. 2008;451:937–42. - PubMed
-
- Mias C, Lairez O, Trouche E, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells promote matrix metalloproteinase secretion by cardiac fibroblasts and reduce cardiac ventricular fibrosis after myocardial infarction. Stem Cells. 2009;27:2734–43. - PubMed
-
- Kuethe F, Richartz BM, Kasper C, et al. Autologous intracoronary mononuclear bone marrow cell transplantation in chronic ischemic cardiomyopathy in humans. Int J Cardiol. 2005;100:485–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

