Inhibiting mitochondrial Na+/Ca2+ exchange prevents sudden death in a Guinea pig model of heart failure
- PMID: 24780171
- PMCID: PMC4219273
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.303062
Inhibiting mitochondrial Na+/Ca2+ exchange prevents sudden death in a Guinea pig model of heart failure
Abstract
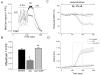
Rationale: In cardiomyocytes from failing hearts, insufficient mitochondrial Ca(2+) accumulation secondary to cytoplasmic Na(+) overload decreases NAD(P)H/NAD(P)(+) redox potential and increases oxidative stress when workload increases. These effects are abolished by enhancing mitochondrial Ca(2+) with acute treatment with CGP-37157 (CGP), an inhibitor of the mitochondrial Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger.
Objective: Our aim was to determine whether chronic CGP treatment mitigates contractile dysfunction and arrhythmias in an animal model of heart failure (HF) and sudden cardiac death (SCD).
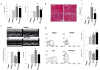
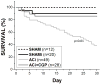
Methods and results: Here, we describe a novel guinea pig HF/SCD model using aortic constriction combined with daily β-adrenergic receptor stimulation (ACi) and show that chronic CGP treatment (ACi plus CGP) attenuates cardiac hypertrophic remodeling, pulmonary edema, and interstitial fibrosis and prevents cardiac dysfunction and SCD. In the ACi group 4 weeks after pressure overload, fractional shortening and the rate of left ventricular pressure development decreased by 36% and 32%, respectively, compared with sham-operated controls; in contrast, cardiac function was completely preserved in the ACi plus CGP group. CGP treatment also significantly reduced the incidence of premature ventricular beats and prevented fatal episodes of ventricular fibrillation, but did not prevent QT prolongation. Without CGP treatment, mortality was 61% in the ACi group <4 weeks of aortic constriction, whereas the death rate in the ACi plus CGP group was not different from sham-operated animals.
Conclusions: The findings demonstrate the critical role played by altered mitochondrial Ca(2+) dynamics in the development of HF and HF-associated SCD; moreover, they reveal a novel strategy for treating SCD and cardiac decompensation in HF.
Keywords: calcium; energy metabolism; heart failure; mitochondria; oxidative stress; reactiveoxygen species; sudden cardiac death.
© 2014 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Bigger JT., Jr Why patients with congestive heart failure die: arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. Circulation. 1987;75:IV28–35. - PubMed
-
- Goldman S, Johnson G, Cohn JN, Cintron G, Smith R, Francis G. Mechanism of death in heart failure. The Vasodilator-Heart Failure Trials The V-HeFT VA Cooperative Studies Group. Circulation. 1993;87:VI24–31. - PubMed
-
- Abraham WT, Wagoner LE. Medical management of mild-to-moderate heart failure before the advent of beta blockers. Am J Med. 2001;110(Suppl 7A):47S–62S. - PubMed
-
- Mann DL, Bristow MR. Mechanisms and models in heart failure: the biomechanical model and beyond. Circulation. 2005;111:2837–2849. - PubMed
-
- Gupta A, Akki A, Wang Y, Leppo MK, Chacko VP, Foster DB, Caceres V, Shi S, Kirk JA, Su J, Lai S, Paolocci N, Steenbergen C, Gerstenblith G, Weiss RG. Creatine kinase-mediated improvement of function in failing mouse hearts provides causal evidence the failing heart is energy starved. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:291–302. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

