Effect of biased feedback on motor imagery learning in BCI-teleoperation system
- PMID: 24782721
- PMCID: PMC3988391
- DOI: 10.3389/fnsys.2014.00052
Effect of biased feedback on motor imagery learning in BCI-teleoperation system
Abstract
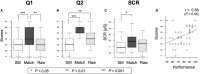
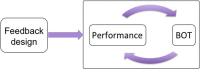
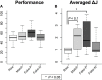
Feedback design is an important issue in motor imagery BCI systems. Regardless, to date it has not been reported how feedback presentation can optimize co-adaptation between a human brain and such systems. This paper assesses the effect of realistic visual feedback on users' BCI performance and motor imagery skills. We previously developed a tele-operation system for a pair of humanlike robotic hands and showed that BCI control of such hands along with first-person perspective visual feedback of movements can arouse a sense of embodiment in the operators. In the first stage of this study, we found that the intensity of this ownership illusion was associated with feedback presentation and subjects' performance during BCI motion control. In the second stage, we probed the effect of positive and negative feedback bias on subjects' BCI performance and motor imagery skills. Although the subject specific classifier, which was set up at the beginning of experiment, detected no significant change in the subjects' online performance, evaluation of brain activity patterns revealed that subjects' self-regulation of motor imagery features improved due to a positive bias of feedback and a possible occurrence of ownership illusion. Our findings suggest that in general training protocols for BCIs, manipulation of feedback can play an important role in the optimization of subjects' motor imagery skills.
Keywords: BCI-teleoperation; body ownership illusion; feedback effect; motor imagery learning; training.
Figures

References
-
- Gonzalez-Franco M., Peng Y., Dan Z., Bo H., Shangkai G. (2011). Motor imagery based brain-computer interface: a study of the effect of positive and negative feedback, in Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Annual International Conference of the IEEE (Boston, MA: ), 6323–6326 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

